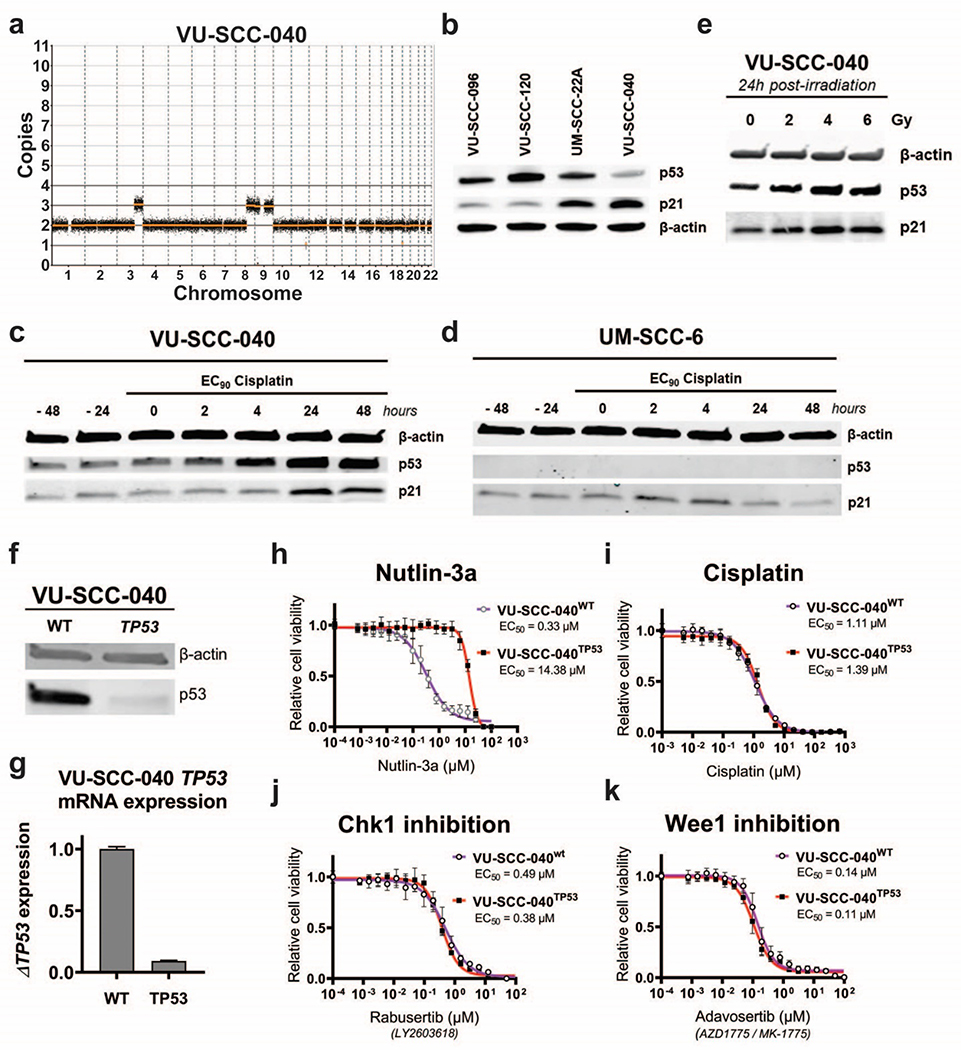
Figure 3. Characterization of HPV-negative, CN-silent and TP53 wild-type cell line VU-SCC-040.
a
Genomic CN-profile of copy number silent cell line VU-SCC-040, which only contains a single gain of 3q, 8q and 9p/q.
b
Western blot analysis of p53 and downstream target p21 in TP53-mutant cell lines VU-SCC-096, VU-SCC-120 and UM-SCC-22A, compared with CN-silent TP53 wild-type lineVU-SCC-040. VU-SCC-040 showed lower levels of p53 compared to the TP53 mutated cell lines, as expected. Furthermore, p21 expression was higher compared to the TP53 mutated cell lines, although UM-SCC-22A showed an intermediated p21 expression level.
c-d
Protein expression of p53 and p21 in TP53 wild-type cell line VU-SCC-040 (c) and TP53-null line UM-SCC-6 (d) was analyzed after treatment of cisplatin with the EC90 concentration for the indicated timespans. Before treatment, levels of p53 and p21 are stable in VU-SCC-040. Upon treatment of cisplatin, p53 expression is increased within 4 hours, and p21 levels increase after 24 hours, strongly suggesting that this part of the pathway is intact. In UM-SCC-6, p53 expression is absent due to a frameshift insertion in exon 1 and consequently, p21 levels do not change upon treatment of cisplatin.
e.
24 hours post-irradiation with 2, 4 and 6 Gy, an increase of p53 was observed for 4 and 6 Gy in VU-SCC-040.
f.
p53 protein expression was investigated in the parental VU-SCC-040wt and CRISPR TP53-knockout line VU-SCC-040TP53. Only a very low p53 expression was observed in the knockout line compared to the wild-type line, in line with the TIDE sequence analysis, and indicating that the majority of cells obtained a TP53 knockout.
g.
mRNA expression of TP53 was significantly reduced in the knockout cell line compared to the parental wild-type VU-SCC-040. Although this is not necessarily observed with a CRISPR-Cas9 approach, it confirms nonsense mediated decay of the RNA levels and the successful knockout of the gene.
h.
VU-SCC-040wt cells are very vulnerable to MDM2 inhibition with Nutlin-3a, as expected for a cell with a functional p53-pathway. For the VU-SCC-040TP53 knockout line, resistance to Nutlin-3a was obtained, in line with the EC50-values of the TP53-mutant HNSCC lines (figure S2f–h).
i.-k.
Dose-response curves of VU-SCC-040wt and VU-SCC-040TP53 showing the relative cell viability after 72h treatment with a dilution range of Cisplatin (i), Chk1 inhibitor Rabusertib (LY2603618) (j) and Wee1 inhibitor Adavosertib (AZD1775 / MK-1775) (k). Surprisingly, no difference in response was found between VU-SCC-040wt and VU-SCC-040TP53, and the EC50 values were within the range of TP53-mutant HNSCC cell lines, and sensitivity much higher than normal cells ([15,37] and van Harten et al., submitted). This indicates that the cell cycle is perturbed in VU-SCC-040, but apparently with an intact p53 pathway.