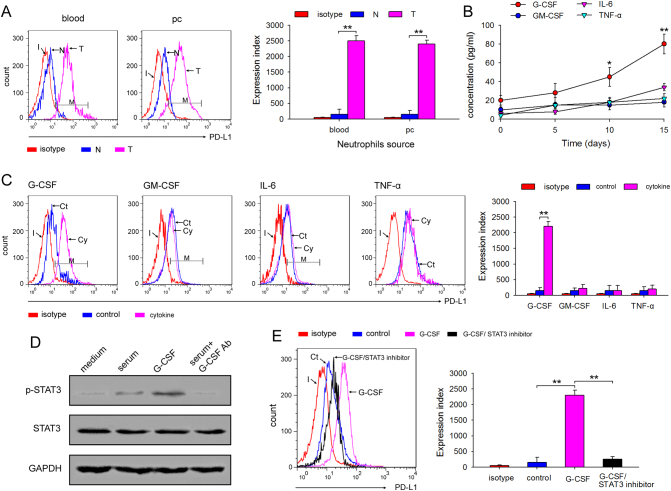
Fig. 4.
Tumor-derived G-CSF induces PD-L1 expression on neutrophils through the STAT3 pathway. (a) The expression of PD-L1 on neutrophils isolated from tumor-bearing mice. The expression of PD-L1 on neutrophils isolated from blood and abdominal cavity of naïve or tumor-bearing mice was analyzed by FCM, and expression index was calculated. (b) The level of G-CSF, GM-CSF, IL-6, and TNF-α in serum tumor-bearing mice. Mice were inoculated with CT-26 cells, and the serum concentration of G-CSF, GM-CSF, IL-6, and TNF-α was detected by ELISA at the indicated times. (c) The effect of G-CSF, GM-CSF, IL-6, and TNF-α on PD-L1 expression on neutrophils. The neutrophils from C-PC of the indicated mice were cultured for 12 h in the presence of G-CSF, GM-CSF, IL-6, and TNF-α, and the expression of PD-L1 on neutrophils was detected by FCM, and expression index was calculated. (d) The effects of G-CSF on STAT3 activation. The neutrophils from C-PC were stimulated with tumor-bearing mice serum, G-CSF or tumor-bearing mice serum plus G-CSF antibody for 12 h, and phospho-STAT3 was detected by WB. (e) The effect of STAT3 inhibitor on PD-L1 expression on neutrophils. The neutrophils from C-PC were cultured for 12 h in the presence of G-CSF or G-CSF plus STAT3 inhibitor FLLL32, and the expression of PD-L1 on neutrophils was detected by FCM, and expression index was also calculated. Results are expressed as mean ± SD from three independent experiments (n = 6 in each group). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.