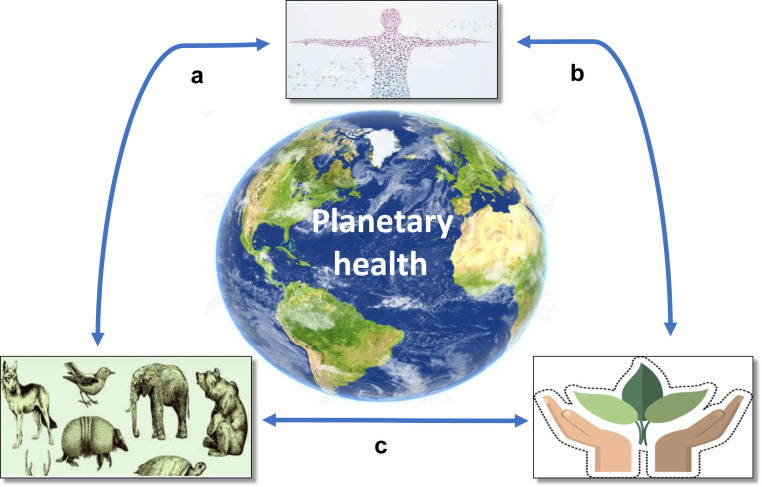
Figure 2.
Lifestyle diseases associated with inflammation, tissue hypoxia, mitochondrial dysfunction, and oxidative stress are intimately linked to the health of animals and the environment. (a) Contained within adaptations in certain species that evolved to survive extreme environmental factors, such as long, cold winters, water shortages, and hypoxia, are survival strategies that could provide clues for human health. (b) Lack of clean water, pollution, and heat stress cause human disease, creating a need for climate medicine. (c) Lack of clean water, pollution, and heat stress cause loss of animal and plant habitat. Habitat loss, illegal trade, natural selection, and evolution affect animal health. Animals that have occupied niches and developed mechanisms to protect themselves against environmental factors, such as lack of water, infections, oxygen deprivation, and heat stress, could provide valuable clues for the protection of humans from environmental changes.