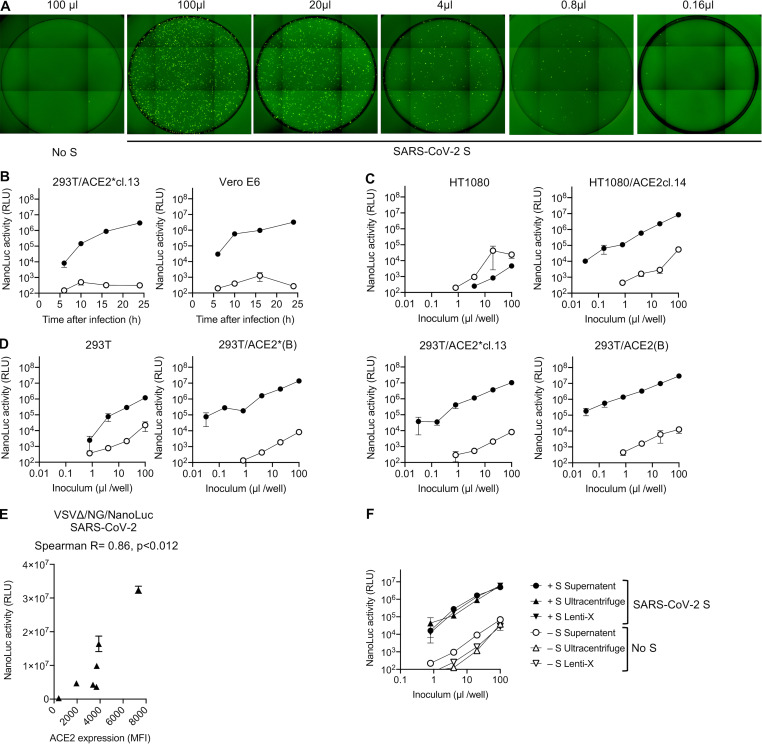
Figure S3.
rVSVΔG/NG-NanoLuc pseudotyped virus infection. (A) Infection of Huh7.5 cells with the indicated volumes of rVSVΔG/NG-NanoLuc pseudotyped virus. Images of the entire well of 96-well plates are shown. (B) Infectivity of rVSVΔG/NG-NanoLuc pseudotyped with SARS-CoV-2 SΔ19 or no S (background control) on the indicated cell lines. Infectivity was quantified at the indicated times post-inoculation by measuring NanoLuc luciferase levels (RLU). Mean and range of two technical replicates are plotted. cl., clone. (C and D) HT1080-derived cell lines (C) or 293T-derived cell lines (D) were infected with varying amounts of rVSVΔG/NG-NanoLuc pseudotyped with SARS-CoV-2 SΔ19 or no S (background control), and NanoLuc luciferase levels were measured at 16 h after infection. Mean and range of two technical replicates are plotted. (E) Relationship between NanoLuc luciferase activity (RLU) and ACE2 cell surface expression levels (quantified by flow cytometry; Fig. S1 A) following infection the cell lines depicted in Fig. S1 A with rVSVΔG/NG-NanoLuc. Mean and range of two technical replicates is plotted. (F) Effect of virus concentration on the infectivity of rVSVΔG/NG-NanoLuc pseudotyped virus. Huh7.5 cells were infected with equivalent doses of either unmanipulated virus-containing supernatant or virions that had been pelleted by ultracentifugation or using Lenti-X and diluted to the original volume. Mean and range of two technical replicates are plotted.