Figure 2.
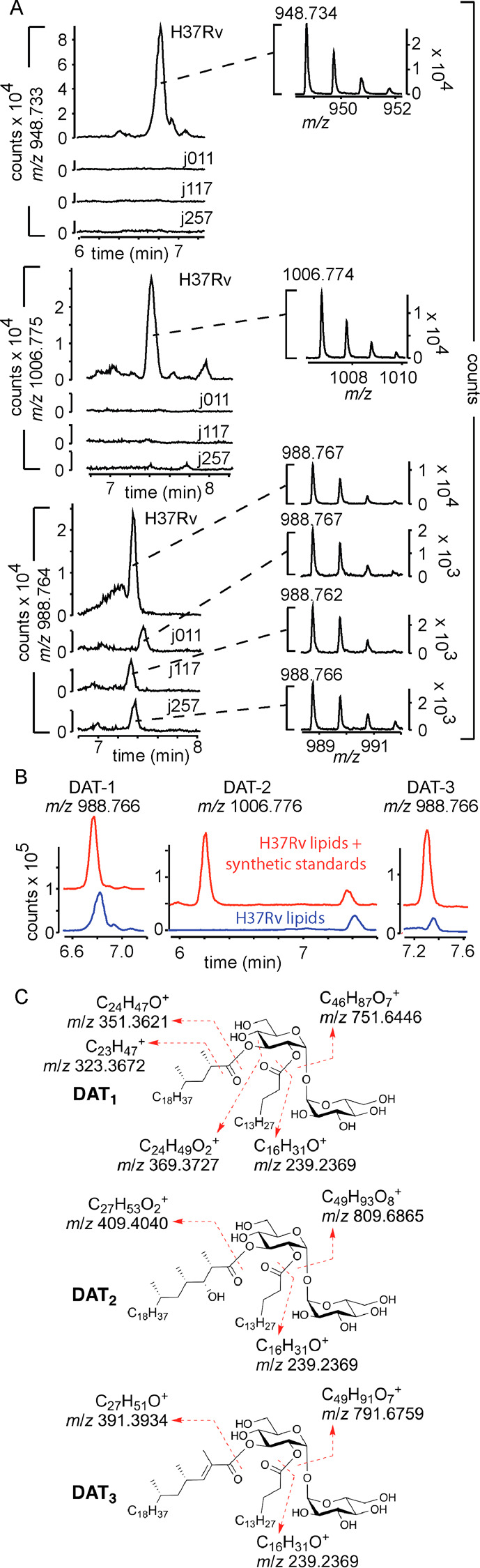
Detection of DAT variants in M. tuberculosis strains. Lipid extracts from four different M. tuberculosis strains were analyzed via high-performance liquid chromatography–mass spectroscopy (HPLC-MS): laboratory strain H37Rv, and three clinical isolates named j257, j011, and j117. Extracted ion chromatograms of ions corresponding with the ammonium adduct of DAT1 (calculated m/z = 948.733), DAT2 (m/z = 1006.775), and DAT3 (m/z = 988.764) showed m/z values consistent with those expected from DATs. (B) Comparison with synthetic standards showed chromatographic coelution for DAT1 and DAT3 but not for DAT2, indicating that synthetic DAT2 is not identical to natural DAT2. (C) CID analysis of the standards and natural compounds (see data given in the Supporting Information) yielded fragmentation patterns diagnostic for the known structures.
