Figure 1.
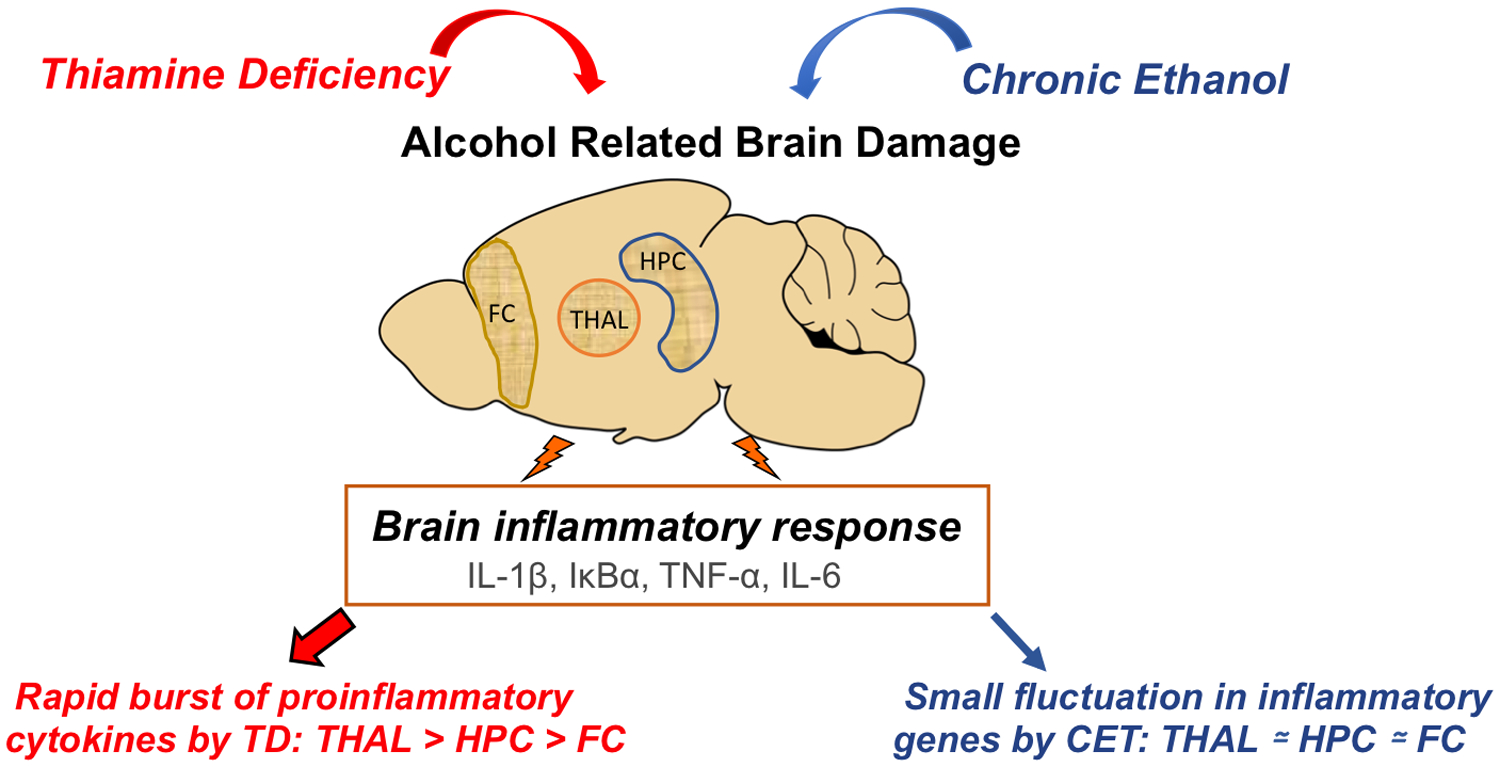
Thiamine deficiency (TD) and chronic ethanol treatment (CET) are critical factors in the induction of alcohol-related brain damage (ARBD) and inflammatory responses in brain. Our findings shown the TD, rather than CET, is a key driver of neuroimmune gene expression and subsequent neuroinflammation across the thalamus (THAL), hippocampus (HPC) and frontal cortex (FC).
