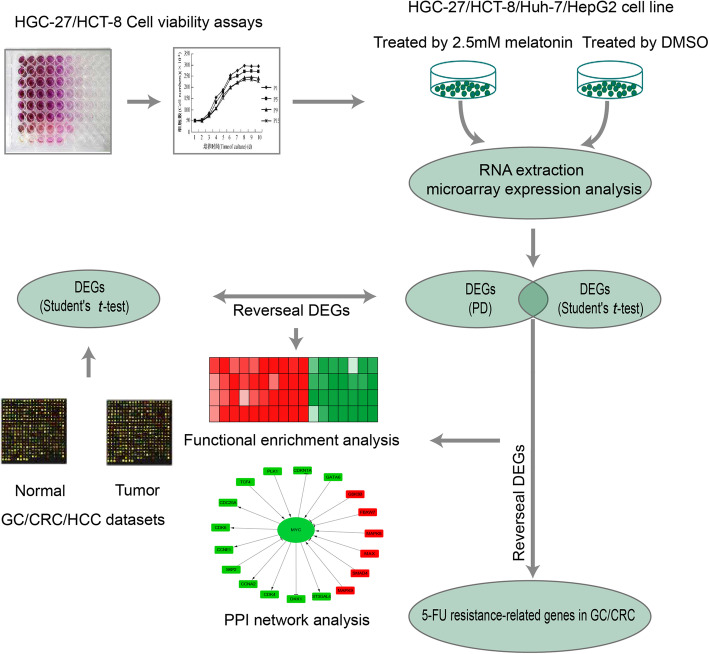
Fig. 1.
The flowchart of this study. First, Melatonin inhibited cell growth of HGC-27 and HCT-8 cells in a dose and time-dependent manner. The concentration (2.5 mmol/L) and time (24 h) of melatonin for treatment were determined. Second, four cancer cell lines (HGC-27, HCT-8, Huh-7 and HepG2) across three types of gastrointestinal carcinomas (GC, CRC and HCC) were treated by melatonin for 24 h and performed by DNA microarray analysis. Third, the DEGs by melatonin treatment detected by Student’s t-test and the reproducibility-based PD were combined to investigate the common biological signaling pathways altered by melatonin. Fourth, the DEGs detected between tumor and normal tissues but reversed by melatonin in cancer cell lines were used to explore the potential anticancer effects of melatonin. Finally, the 5-FU resistance-related genes in GC and CRC but reversed by melatonin in cancer cell lines were used to explore the potential of melatonin to increase the sensitivity of 5-FU in GC and CRC