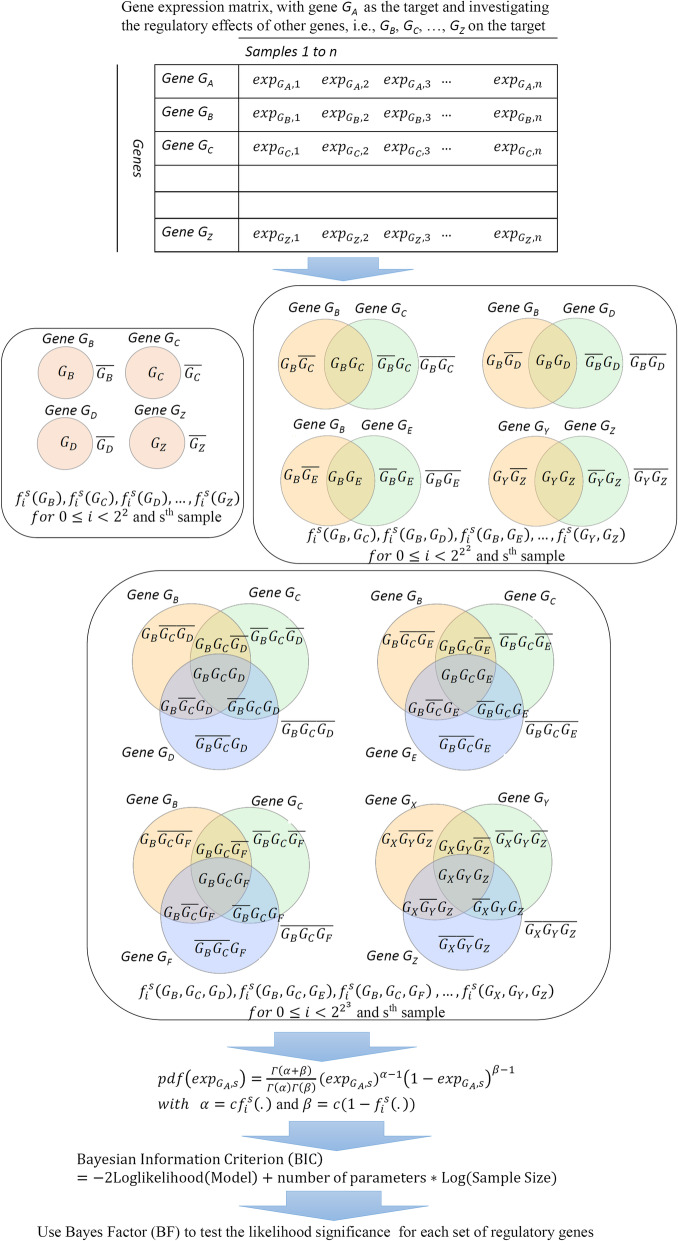
Fig. 7.
Workflow diagram of the LogicNet to reconstruct the Gene Regulatory Network. Assume n samples are drawn from the expression level of genes GA, GB, …, and GZ. Each time, one gene is considered as the target, and the regulatory effect of other genes on the target is investigated. Here, gene GA is considered as the target. Logic functions consisting of k regulatory genes are constructed for k = 1, 2, 3, and the target gene expression likelihoods are evaluated under different logic functions. To calculate the likelihood, the target’s gene expression is modeled by using a beta distribution whose parameters are identified based on the logic function between the regulatory genes. Then, the Bayesian Information Criterion (BIC) is applied to strike the right balance between the likelihood and model complexity (the number of the regulatory genes). For each target gene, the likelihood significance in the logic function with the lowest BIC is further evaluated by using the Bayes Factor (BF). Only logic functions which are decisively supported by the target gene expression data (with BF > 100) are considered to be significant