FIGURE 4.
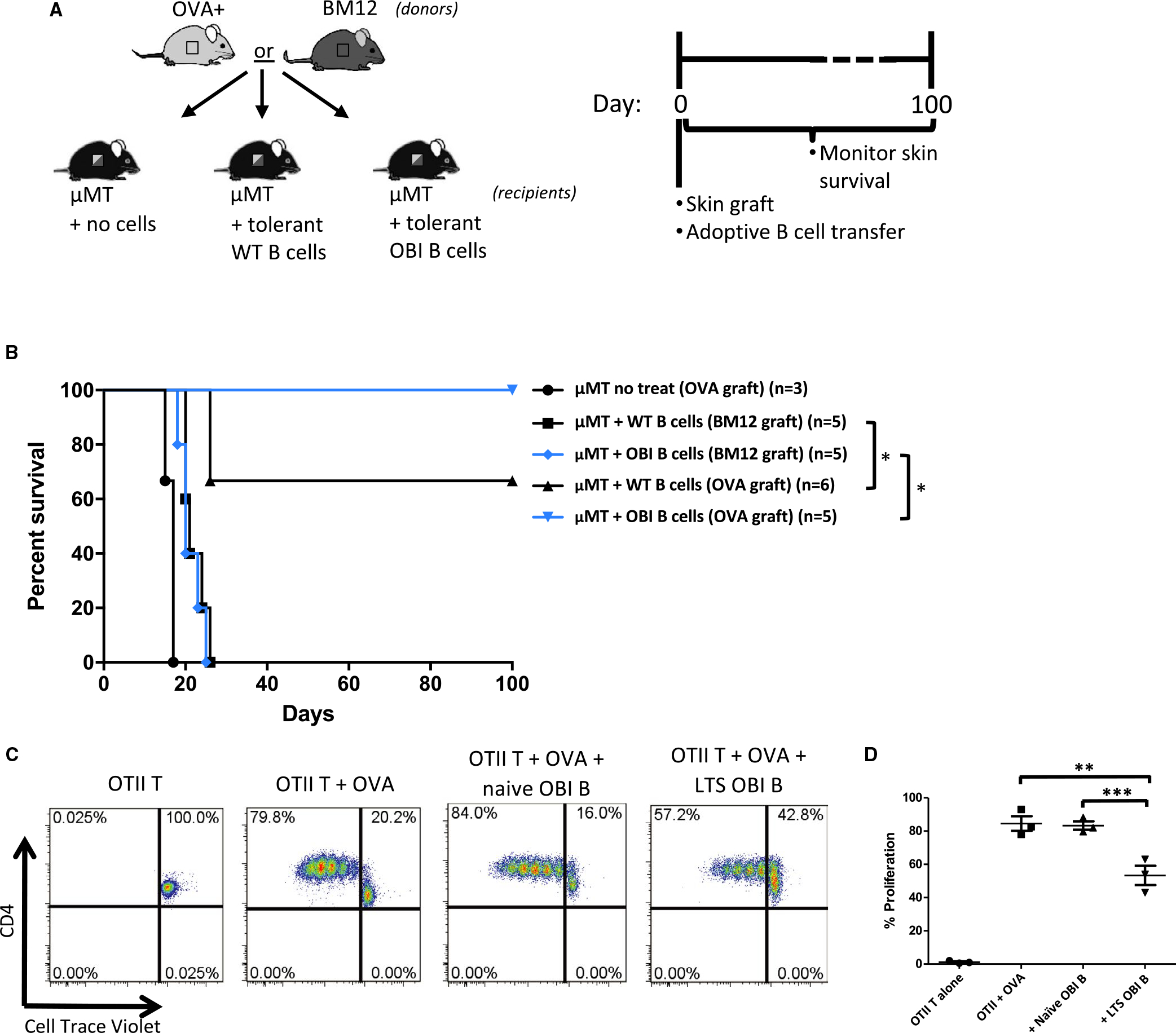
A, Diagram and timeline for B cell adoptive transfer experiments. Skin from OVA+ or BM12 mice is grafted at the same time as 5 × 106 B cells from tolerant mice (mice previously made tolerant to OVA+ skin grafts). Monitored for 100 d. B, OVA+ or BM12 skin graft survival after adoptive transfer of tolerant B cells. B cells isolated from WT C57BL/6 and OBI mice previously grafted with OVA+ skin, confer tolerance to OVA+ skin grafts when adoptively transferred into μMT mice (denoted with “OVA graft”). μMT mice that receive skin grafts from BM12 donors (denoted with “BM12 graft”) fail to develop tolerance after adoptive transfer of tolerant WT or OBI B cells. OVA+ skin grafts on untreated μMT mice fail to survive beyond 20 days. C, B cells from OBI mice with long-term surviving grafts (LTS) are capable of suppressing proliferation of CD4+ OTII T cells when stimulated by OVA-expressing splenocytes in vitro. OTII T cells are labeled with Cell Trace Violet and co-cultured with irradiated OVA+ splenocytes with or without an equal number of B cells from either naive OBI mice or from LTS OBI mice. D, Summary of 3 experiments. *P < .05; **P = .0128, ***P = .009. OBI, ovalbumin (OVA)-specific BCR mice; OVA, ovalbumin; WT, wild type; μMT, B6.129S2-Ighmtm1Cgn/J
