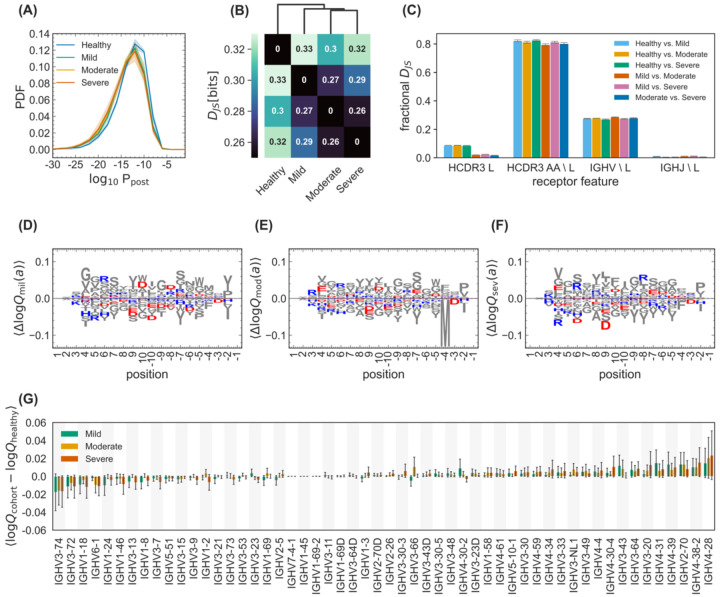
Figure 3. Differential statistics of immune repertoires across cohorts.
(A) The distribution of the log-probability to observe a sequence σ in the periphery log10 Ppost(σ) is shown as a normalized probability density function (PDF) for inferred naïve progenitors of clonal lineages in cohorts of healthy individuals and the mild, moderate, and severe cohorts of COVID-19 patients. Full lines show distributions averaged over individuals in each cohort, and shadings indicate regions containing one standard deviation of variation among individuals within a cohort. (B) Clustering of cohorts based on their pairwise Jensen-Shannon divergences DJS as a measure of differential selection on cohorts is shown (Methods). (C) The bar graph shows how incorporating different features into a SONIA model contributes to the fractional Jensen-Shannon divergence between models trained on different cohorts. The error bars show the variations of these estimates over five independently inferred models (Methods). Logo plots show the expected differences in the log-selection factors for amino acid usage, 〈Δlog Qcohort(a)〉 = 〈log Qcohort(a) − log Qhealthy(a)〉 for the (D) mild, (E) moderate, and (F) severe COVID-19 cohorts. The expectation values 〈•〉 are evaluated on the mixture distribution . Positively charged amino acids (lysine, K; arginine, R; and histidine, H) are shown in blue while negatively charged amino acids (aspartate, D, and glutamate, E) are shown in red. All other amino acids are grey. Positions along the HCDR3 are shown up to 10 residues starting from the 3’ (positive position values) and the 5’ ends (negative position values). (G) The bar graph shows the average mean difference between the log-selection factors for IGHV-gene usage for the mild (green), moderate (yellow), and severe (red) COVID-19 cohorts, with the mean computed using the mixture distribution and the average taken over the mean differences of 30 independently trained SONIA models for each cohort. Error bars show one standard deviation for the estimated mean, due to variations in the inferred SONIA models.