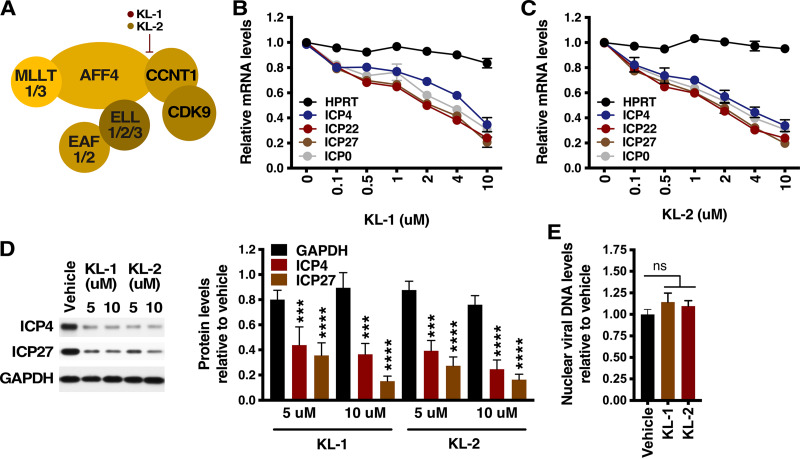
FIG 1.
Inhibitors of the SEC suppress HSV IE gene expression. (A) KL-1 and KL-2 interfere with the interaction of CCNT1/P-TEFb with SEC scaffold subunit AFF4. (B to D) HFF cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of KL-1 (B) or KL-2 (C) and infected with HSV (MOI = 1) for 2.5 h. (B and C) mRNA levels of viral IE genes (ICP4, ICP22, ICP27, and ICP0) and a control cellular gene (HPRT) relative to those in vehicle-treated cells. Sample mRNA levels were normalized based on the levels of cellular GAPDH (glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase) mRNAs. Data are means ± SEM of results from at least two experiments. (D) (Left) Western blot of viral IE (ICP4 and ICP27) and cellular control (GAPDH) protein levels. (Right) Quantitation of protein levels in cells treated with KL-1 or KL-2 relative to those in cells treated with vehicle. Data are means ± SEM of results from four replicates (analysis of variance [ANOVA] with Dunnett’s post hoc test). (E) HFF cells were treated with vehicle or 8 μM KL-1 or KL-2 and infected with HSV (MOI = 1) for 2 h. Nuclear HSV DNA levels in cells treated with KL-1 or KL-2 relative to those in cells treated with vehicle are indicated. ns, not significant (ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc test).