Fig. 1.
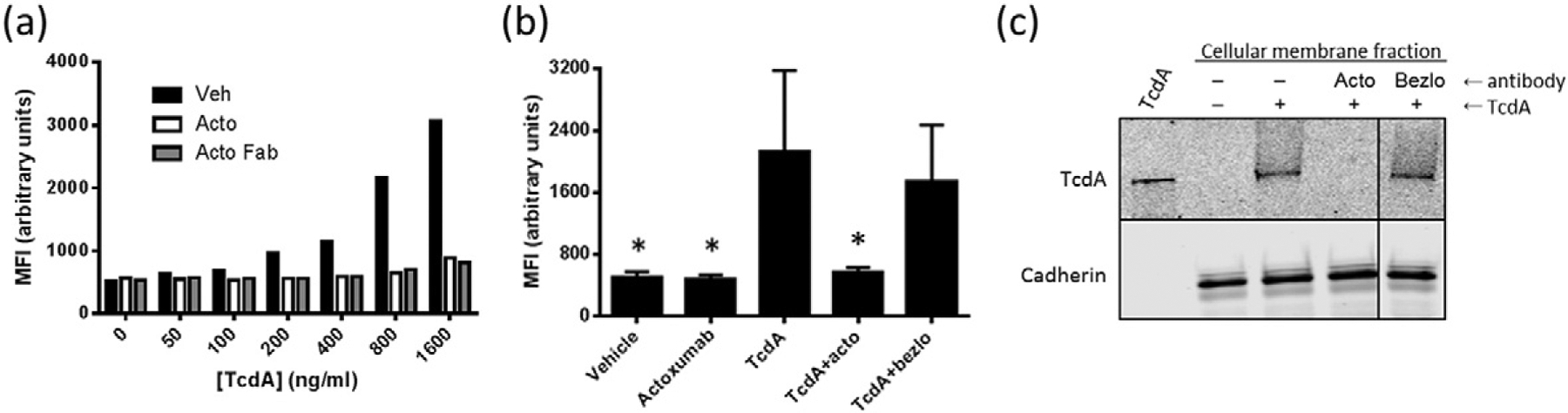
Actoxumab prevents the binding of TcdA to HT29 and Vero cells. (a) Flow cytometry analysis of HT29 cells preincubated with increasing concentrations of TcdA-Atto488 at 4 °C in the presence or absence of vehicle, actoxumab (200 μg/ml), or actoxumab-Fab (200 μg/ml). Following incubation, MFI was measured with excitation and emission wavelengths of 488 nm and 530 nm, respectively. A representative experiment is shown. (b) Flow cytometry analysis of HT29 cells preincubated with 800 ng/ml TcdA-Atto488 at 4 °C in the presence or absence of vehicle, actoxumab, or bezlotoxumab. MFIs were calculated as per panel (a). Values are means ± standard deviation of two independent experiments. acto = actoxumab; bezlo = bezlotoxumab. *p < 0.05 compared to TcdA alone by paired two-tailed t-test. (c) Western blot of membranes isolated from Vero cells following incubation with 1 μg/ml TcdA in the presence of vehicle, actoxumab, or bezlotoxumab (200 μg/ml). The top panel shows TcdA and the bottom panel shows cadherin (loading control).
