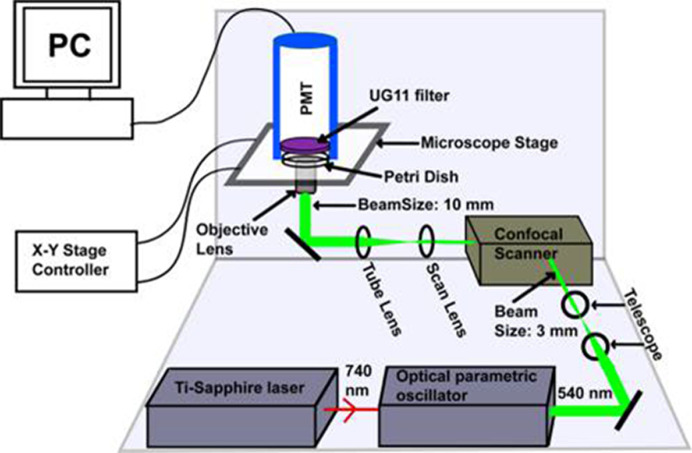
Figure 6. Schematic representation of the optical setup for dopamine imaging (not to scale).
An optical parametric oscillator synchronously pumped by mode-locked tunable Ti-Sapphire laser at 740 nm produces 540 nm ∼100 fs pulses. The collimated beam (3 mm in diameter, achieved using a telescope setup) is routed through a confocal scan-box to an inverted microscope equipped with a 60× water immersion objective lens (numerical aperture, NA = 1.2). The beam diameter is 10 mm at the back of the objective lens and has an average power of 30 mW. The emission is collected in the forward direction, with an external photomultiplier tube (PMT) placed directly above the sample. A pair of special glass based absorptive filters (UG11) is placed in front of the PMT which transmits the mid-UV fluorescence but efficiently blocks the 540 nm excitation light. (Reprinted with permission from Sarkar, B.; Banerjee, A.; Das, A.K.; Nag, S.; Kaushalya, S.K.; Tripathy, U.; Shameem, M.; Shukla, S.; Maiti, S. (2014) Label-free dopamine imaging in live rat brain slices. ACS Chem. Neurosci., 5(5), 329–334 [49]. Copyright (2014) American Chemical Society.)