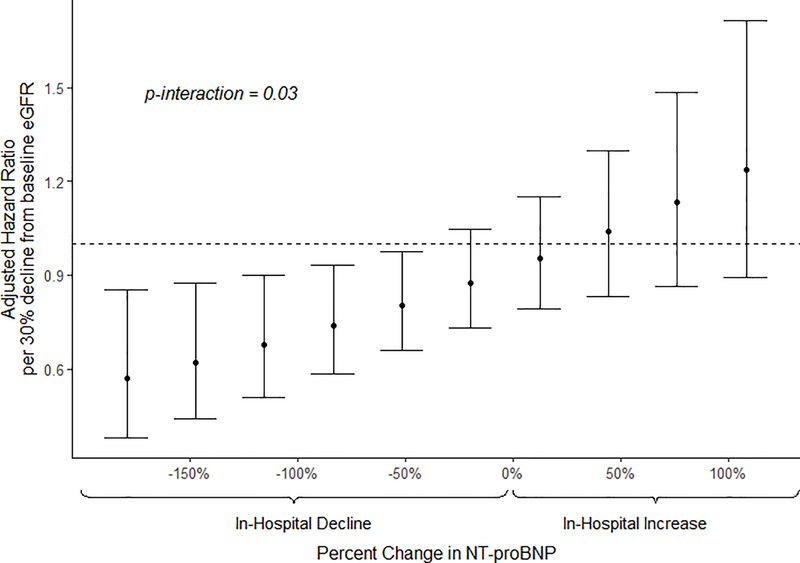
Figure 3.
Adjusted hazard ratios for composite outcome of death or re-hospitalization for each 30% decline in eGFR by varying levels of change in NT-ProBNP.
Multivariable adjusted Cox regression model including the interaction (p=0.03) between decline in eGFR and change in NT-proBNP. Both eGFR and NT-proBNP were log-transformed; eGFR by base 10/7 enabling hazard ratios to be assessed for a 3/10 decline, synonymous to a 30% decline. HR: hazard ratio; eGFR: estimated glomerular filtration rate; NT-proBNP: N-terminal prohormone of brain natriuretic peptide.