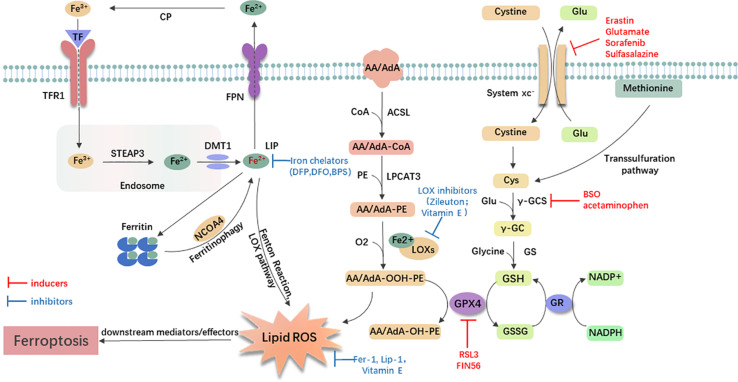
FIGURE 1.
General mechanism of ferroptosis associated with lipid, amino acid, and iron metabolism. The inactive Fe3+ is delivered into the cell by TFR1 and reduced to Fe2+ in the endosome. Then, DMT1 transports Fe2+ to the labile iron pool (LIP). Autophagic degradation of ferritin (ferritinophagy) releases Fe2+ from ferritin, which is mediated by NCOA4. Fe2+ produces lipid ROS via the Fenton reaction and through the LOX pathway. Moreover, ACSL4 is required to activate polyunsaturated fatty acid, especially AA and AdA, to AA/AdA-CoA, then LPCAT3 catalyzes these derivatives and membrane PEs to form AA/AdA-PE, which are further converted into pro-ferroptotic lipid peroxidation under the activity of iron-containing LOXs. In conclusion, the Fenton reaction and oxidation of lipids facilitate the generation of lipid ROS, thus leading to ferroptosis. The system xc- is a cystine/glutamate antiporter. Intracellular cystine is reduced to cysteine for the biosynthesis of GSH. GPX4 converts two GSH molecules to GSSG each catalytic cycle to reduce lipid hydroperoxides, and then GSSG can be recycled back via GSH reductase in an NADPH-dependent manner. Ferroptosis inducers inhibit the GPX4-GSH-cysteine axis, thus inhibiting the reduction of lipid ROS. AA/AdA, arachidonic acid or adrenic acid; AA/AdA-CoA, arachidonic acid or adrenic acid coenzyme A; AA/AdA-PE, arachidonic acid or adrenic acid-phosphatidylethanolamine; AA/AdA-OOH-PE, arachidonic acid or adrenic acid-hydroperoxides-phosphatidylethanolamine; AA/AdA-OH-PE, arachidonic acid or adrenic acid-hydroxides-phosphatidylethanolamine; ACSL4, acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 4; BSO, buthionine sulfoximine; CoA, coenzyme A; Cp, ceruloplasmin; Cys, L-cysteine; DMT1, divalent metal transporter 1; Fer-1, ferrostatin-1; FPN, ferroportin; γ-GC, gamma-glutamylcysteine; γ-GCS, gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase; Glu, L-glutamate; GPX4, glutathione peroxidase 4; GR, glutathione reductase; GS, glutathione synthetase; GSH, reduced glutathione; GSSG, di-glutathione; LIP, labile iron pool; Lip-1, liproxstatin-1; LOX, lipoxygenase; LPCAT3, lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 3; NCOA4, nuclear receptor coactivator 4; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; RSL3, RAS-selective lethal 3; STEAP3, 6-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 3; TF, transferrin; TFR1, transferrin receptor 1.