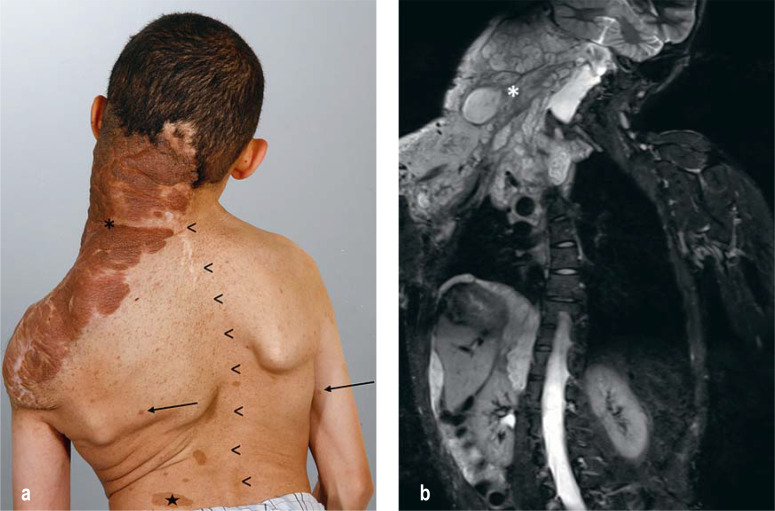
Figure 1:
Features of type 1 neurofibromatosis (NF1)
a) There are small, nodular cutaneous neurofibromas (arrows) and changes of skin pigmentation. A large plexiform neurofibroma (*) extends across the right side of the neck to the back and arm. Scoliosis (arrowheads) and café-au-lait spots (star) are also seen, but are not specific and occur in other genetic syndromes as well (Silver–Russell syndrome, multiple endocrine neoplasia type IIb [MEN IIb], Legius syndrome, McCune–Albright syndrome, etc.).
b) MRI reveals the nodular-infiltrative growth pattern of the plexiform neurofibroma (PNF). Further tumor manifestations are seen around the thoracic and abdominal organs.