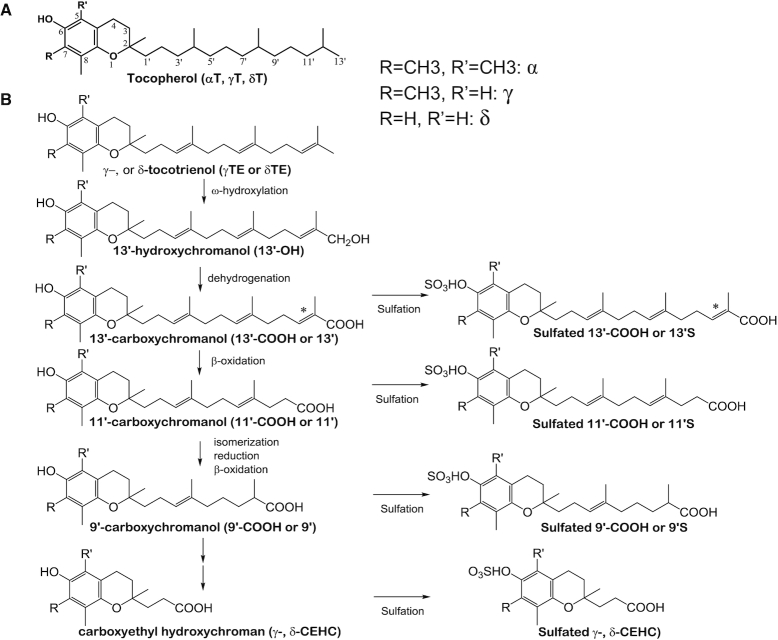
FIGURE 1.
Molecular structures of vitamin E forms and vitamin E metabolism. (A) Structures of αT, γT, and δT. (B) Structures of γTE and δTE, and their metabolism. Tocopherols and tocotrienols are metabolized by ω-hydroxylation and dehydrogenation to form 13′-OH and 13′-COOH, which is then further metabolized by β-oxidation to form 11′-COOH, 9′-COOH, and the terminal metabolite CEHC as well as conjugated carboxychromanols. Compared with tocopherols, catabolism of tocotrienols involves isomerization and reduction, in addition to β-oxidation. *This position may have either a double bond or a saturated bond. CEHC, 2-(β-carboxyethyl)-6-hydroxychroman, also called 3′-COOH; COOH, carboxychromanol; 13′-OH, 13′-hydroxychromanol; αT, α-tocopherol; γT, γ-tocopherol; γTE, γ-tocotrienol; δT, δ-tocopherol; δTE, δ-tocotrienol.