Figure 4.
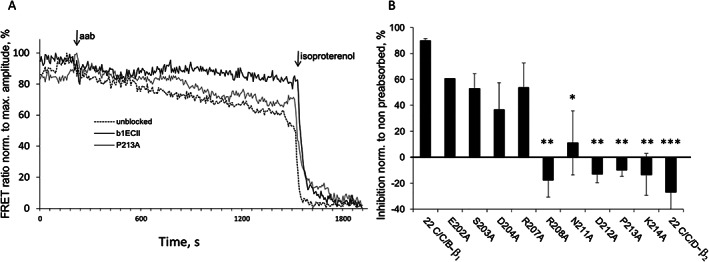
Neutralization of human anti‐β1‐aabs from DCM patients by 22‐mer cyclopeptides mimicking β1ECII with non‐conserved amino acids (compared with the amino acids constituting the ECII loop of the β2‐AR) sequentially replaced by alanine: human anti‐β1‐aabs (IgG fractions) were pre‐absorbed with the indicated cyclopeptide mutants (40 mol/mol IgG, 4°C, 16 h). Anti‐β1‐aab‐induced cAMP production was measured in HEK293 cells expressing the native β1‐AR functionally coupled to a cAMP FRET sensor. (A) Representative recordings of FRET ratios obtained upon addition of anti‐β1‐aabs prepared from a male DCM patient followed by the maximal signal achieved with 1.0 μM of (−)‐isoproterenol (Iso). (B) Prevention of cAMP stimulation after pre‐absorption of patient anti‐β1‐aabs. Results are normalized to the values without pre‐absorption. Columns represent mean ± SEM from at least three to four independent experiments with IgG prepared from different exemplary DCM patients (two men and one woman). Differences between the non‐mutated 22 C/C/B‐β1 cyclopeptide and CP mutations were analysed by one‐way ANOVA with subsequent Dunnett's post‐hoc test for multiple comparisons; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. Internal negative control: non‐mutated 22C/C/D‐β2 (sequence and alignment, see Table S1).
