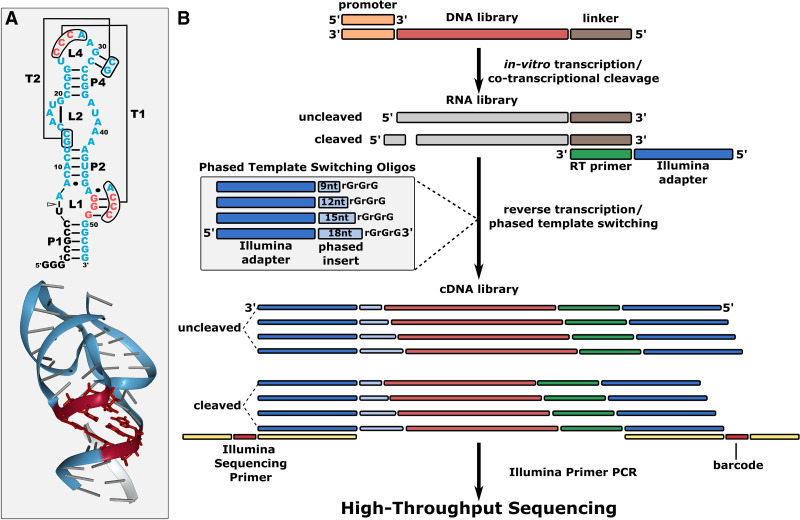
FIGURE 1.
Twister ribozyme library design and in vitro protocol. (A) Secondary and tertiary structure of the twister Osa-1-4 ribozyme (Liu et al. 2014; Rose and Hildebrand 2015). The library contained six randomized nucleotide positions indicated by the red nucleotides. The triangle in the secondary structure indicates the cleavage site, and the black nucleotides are the cleaved product. (B) Illustration of the protocol for cotranscriptional self-cleavage and phased nucleotide insertion during template switching reverse transcription.The DNA library is ordered as the template strand for transcription, with the T7 promoter at the 3′-end, and a primer binding sequence at the 5′-end (linker). Active variants self-cleave during transcription by T7 RNA polymerase. Cleaved and uncleaved RNA products are reverse-transcribed with template switching using the linker sequence for primer binding, and a pool of four phased template switching oligonucleotides. These phased inserts are incorporated into the the cDNA transcripts during reverse transcription. The resulting single stranded cDNA products with phased inserts are amplified with index primers to add full adaptors for high-throughput sequencing (Illumina).