Figure 1.
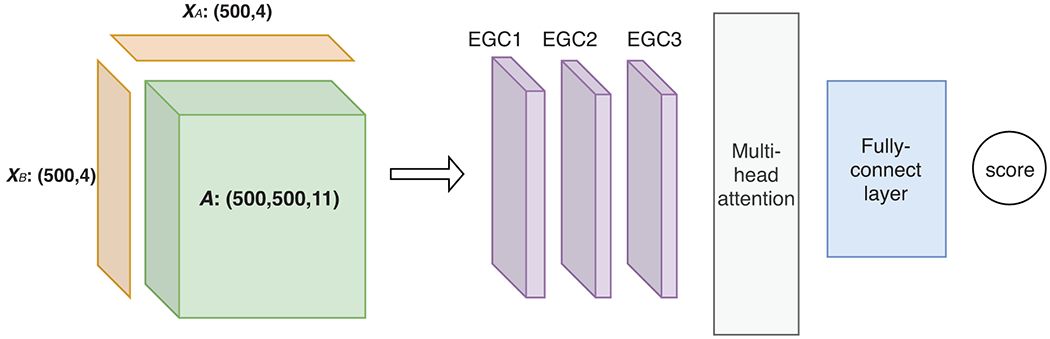
The architecture of the proposed graph convolutional network (GCN) models for intra- or inter-molecular energies. In our work, there are five types of such models together for predicting encounter-complex binding energy, including 4 intra-molecular models with shared parameters for the unbound or encountered receptor or ligand as well as 1 inter-molecular model for the encounter complex. In each type of model, the inputs (to the left of the arrow) include a pair of node-feature matrices (XA and XB) for individual protein(s) and an edge-feature tensor (A) for intra- or inter-molecular contacts. And the inputs are fed through 3 layers of our energy-based graph convolution layers that learn from training data to aggregate and transform atomic interactions, followed by multi-head attention module and fully-connected layers for the output of intra- or inter-molecular energy.
