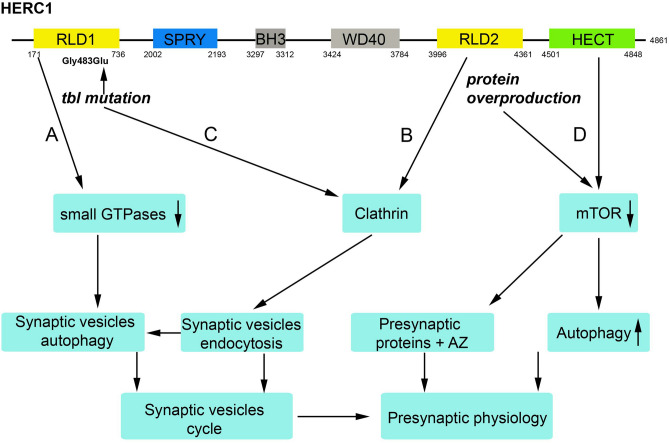
Figure 11.
Schematic representation of the four pathways that the tbl mutation might dysregulate allowing to an increase of the autophagy of synaptic vesicles and the alteration on the number of healthy releasable synaptic vesicles. (A) Mutation site is located at RLD1 domain which dysregulating small GTPS might in turn dysregulate synaptic vesicles homeostasis. (B) RLD2 domain binds clathrin; therefore, alterations of RLD2 alone or by protein overproduction could alter endocytosis during synaptic vesicle recycling. (C) CLT-HERC1 interaction is impaired by mutated RLD1 and in turn could interfere the CME pathway. (D) mTORC1 activity decreased in tbl mutation and could thus explain the increase of autophagosomes; otherwise, mTORC1 participates in autophagy of presynaptic proteins whose dysregulation might contribute to the decrease in size of the active zone (AZ).