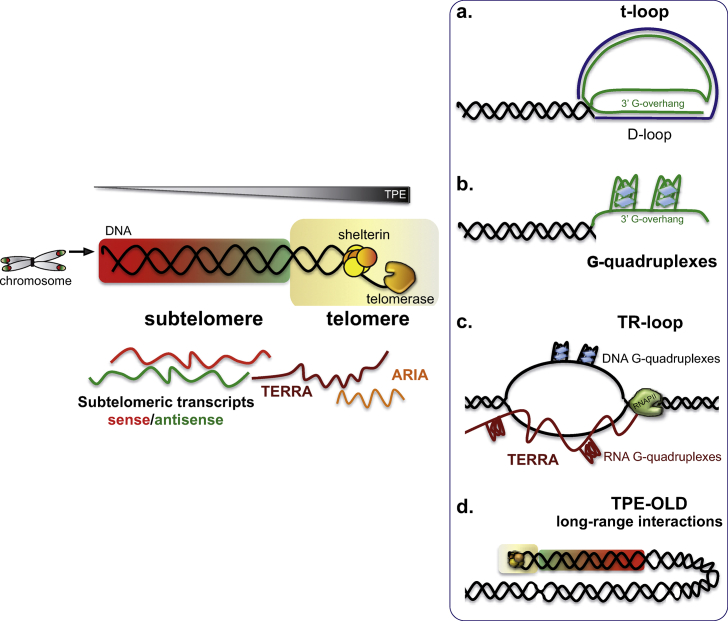
Fig. 1.
Overview of telomeric structures and potential molecular mechanisms of action of telomeric and subtelomeric transcripts. Schematic representation of a chromosome highlighting the telomeres (rainbow squares) at its extremities. Telomeres (in yellow) are composed of tandem repeats bound by shelterin complex and telomerase, which elongates telomeric DNA. TPE intensity decreases toward the centromere. a. Schematic representation of a telomeric t-loop, including a displacement loop (D-loop). b. G-quadruplexes formed on a telomeric 3′G-overhang. c. Telomeric R-loop (TRL) constituted by RNAPII-transcribed TERRA and telomeric sequences. Additionally, G-quadruplexes can be formed by a single G-rich strand. d. Schematic DNA loop representing TPE-OLD and other telomere long-range interactions.