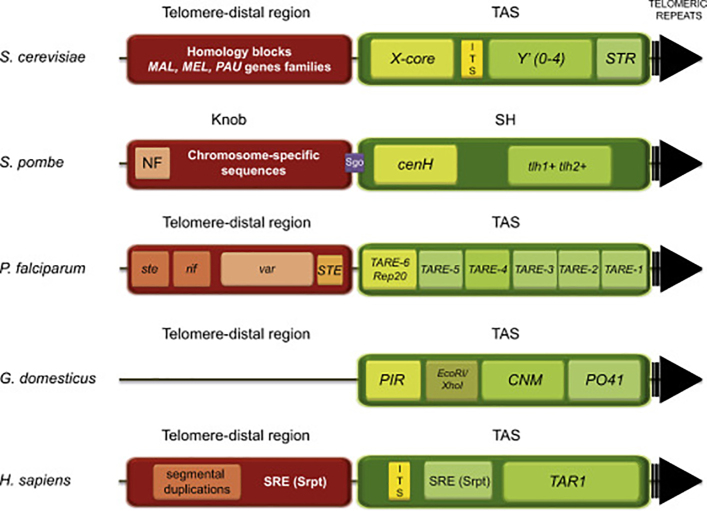
Fig. 2.
Organization of subtelomeric regions in various organisms. In general subtelomeres are composed of two regions: a telomere-proximal region also called TAS (for Telomere-Associated Sequences; in green) and a telomere-distal region (in red). Telomeric repeats are represented as a black arrow. In yeast S. cerevisiae, TAS can be found in two flavors: TAS containing Y′ elements or not (X-only subtelomeres). The X-core element contains ARS (ACS) sequences binding the Abf1 protein and STR repeats with Tbf1 protein-binding sites. The telomere-distal region encloses subtelomeric genes families. ITS (Interspersed/Interstitial/Internal Telomeric Repeats; in yellow) are more or less degenerated telomeric repeats present in TAS between X and Y′ elements. In S. pombe, TAS are called SH regions and contain cenH (centromere-homologous sequence) and telomere-linked helicases (tlh) encoded at chromosomes I (tlh1+) and II (tlh2+). These putative helicases are members of the recQ family and show sequence homology with the dh and dg repeats found at centromeres [186]. The Sgo domain, shown in violet, represents a Sgo2-binding barrier, which controls the spreading of subtelomeric heterochromatin between proximal and distal regions. The telomere-distal region called “knob” contains chromosome-specific sequences and the nucleosome free region (NF) at its centromere-proximal end. In P. falciparum, six telomere-associated repeat elements (TARE1-6/Rap20) and several 12-base SPE sites (binding SPE2 interacting protein 2, PfSIP2) are located between var genes and TAS. 60 var genes are positioned in telomere-distal regions within subtelomeres; rif and ste genes are frequently found in their vicinity [187]. In G. domesticus, tandem repeats PO41, CNM, EcoRI/XhoI and PIR compose TAS. In H. sapiens, Subtelomeric Repeats (SRE/Srpt) comprise about 25% of the most distal 500 kb and 80% of the most distal 100 kb of the chromosome ends [50]. ITS repeats are found between different genetic elements. The TAR1 element, immediately adjacent to the telomeric repeats, is a variably sized (0–2 kb) sequence segment bearing similarity to the TAR1 repeat family.