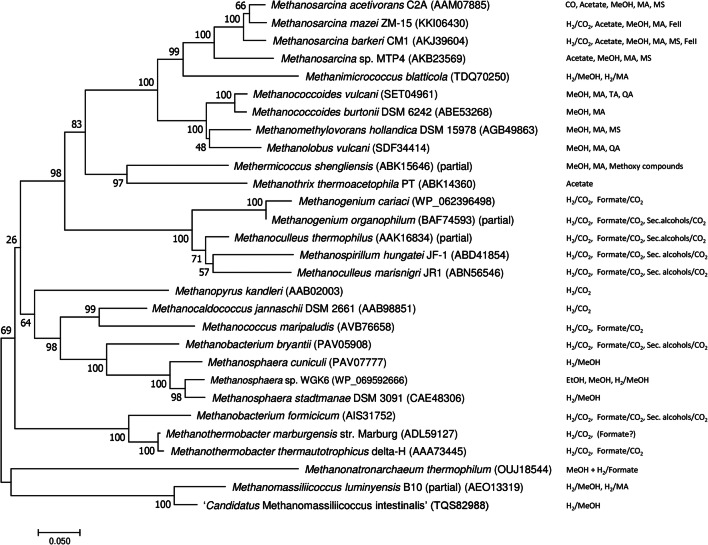
Fig. 2.
Evolutionary relationships of methyl-coenzyme M reductase (subunit A) of different methanogens. The evolutionary history was inferred using the Neighbor-Joining method. The optimal tree with the sum of branch length = 3.29201331 is shown. The percentage of replicate trees in which the associated taxa clustered together in the bootstrap test (500 replicates) are shown next to the branches. The tree is drawn to scale, with branch lengths in the same units as those of the evolutionary distances used to infer the phylogenetic tree. The evolutionary distances were computed using the Dayhoff matrix-based method and are in the units of the number of amino acid substitutions per site. The analysis involved 29 amino acid sequences. All ambiguous positions were removed for each sequence pair. There were a total of 583 positions in the final dataset. Evolutionary analyses were conducted in MEGA7 (Kumar et al. 2016). MA: methylamines, MS: methylated sulfur compounds, TA: tertiary amines, QA: quaternary amines