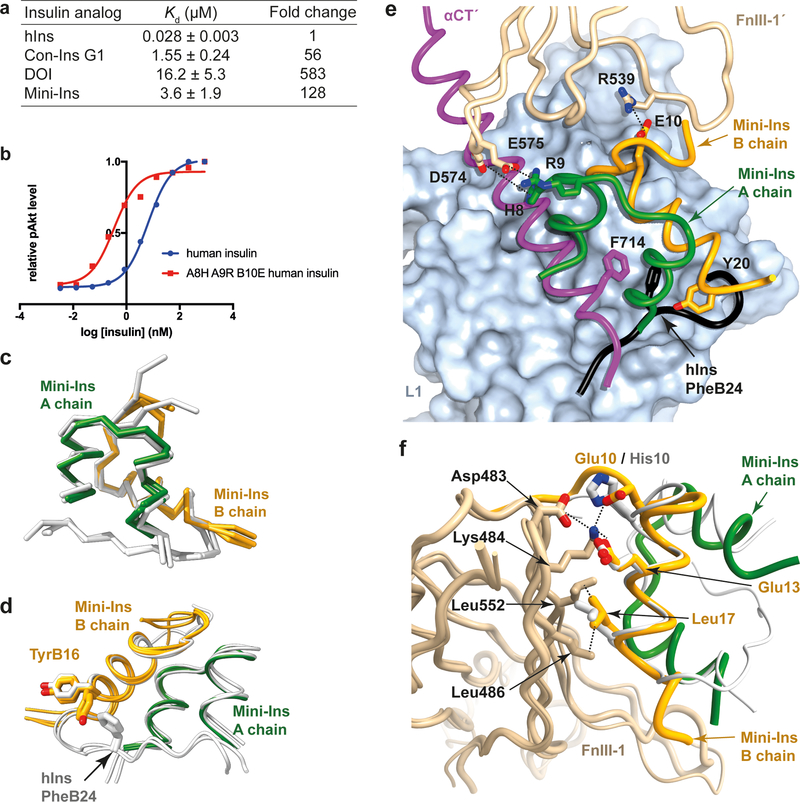
Figure 7. Probing the interaction of mini-Ins with hIR.
(a) Isothermal titration calorimetry studies of various insulin analogs binding to the primary binding site of hIR. Reported Kd values are the weighted mean of the Kd values of individual technical replicates, plus the standard error of that mean (see Methods for further detail). (b) Positive effects of mutations on human insulin. (c) Superposition of the three monomers of mini-Ins (colored) within the asymmetric unit of its crystal structure compared with those within the asymmetric unit of the human insulin crystal structure (white; PDB entry 1MSO). (d) Rotameric variation between TyrB16 within the mini-ins and human insulin crystal structures. Monomers overlaid as in panel (c). (e) Model of mini-Ins in complex with primary and secondary binding site elements of hIR. Domain L1 is shown as surface (powder blue), with ribbon representations of the αCT segment (magenta), mini-Ins A chain (green), mini-Ins B chain (orange) and domain FnIII-1’ (tan). The C-terminal segment of the human insulin B chain (obtained by superimposition of hIns.μIR.Fv83–7) is shown in black, highlighting how TyrB20 of mini-Ins approaches the key hydrophobic pocket occupied by human insulin PheB24. Specific interactions between mini-Ins with FnIII-1’ are highlighted. (f) Model of mini-Ins in complex with transient binding site on domain FnIII-1 of hIR, overlaid human insulin (white) as visualized in PDB entry 6PXV8. Mini-Ins and FnIII-1 colors are as in panel (e). Source data for panels a and b are available with the paper online.