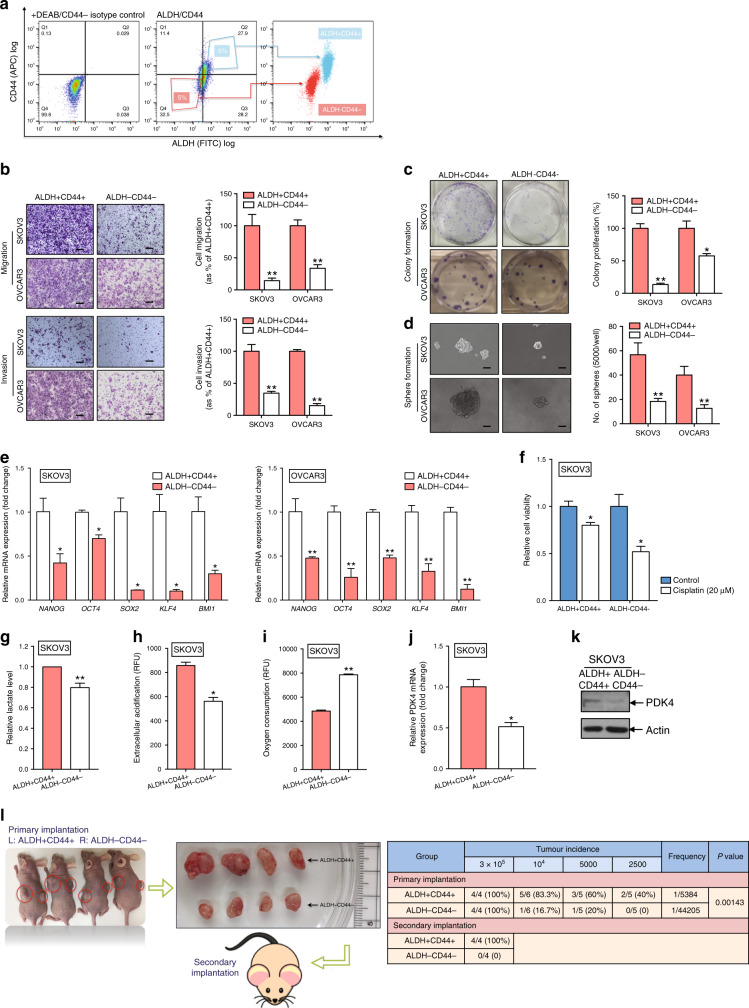
Fig. 2. ALDH+CD44+ cells derived from ovarian cancer cells shows enhanced CSC properties and PDK4 expression.
a FACS-mediated isolation of ALDH+CD44+ and ALDH−CD44− SKOV3 cells. (Left) Isotype control stained with DEAB and FITC IgG. (Middle) The top 5% cells most brightly stained for ALDH+CD44+ or bottom 5% with minimal staining for ALDH−CD44− cells were collected. (Right) Purity of ALDH and CD44 was confirmed via post sorting using flow cytometry. b Transwell migration/invasion (scale bar, 100 μΜ) and c clonogenic assays of ALDH+CD44+ and ALDH−CD44− cells isolated from SKOV3 and OVCAR3 cells were imaged and presented as a percentage of ALDH−CD44− groups. d Sphere formation assay of ALDH+CD44+ and ALDH−CD44− cells isolated from SKOV3 and OVCAR3 cells, followed by imaging (scale bar, 50 μΜ) and quantification of the number of cells that formed tumourspheres. e mRNA expression of relative stemness genes, NANOG, OCT4, SOX2, KLF4, and BMI1, in ALDH+CD44+ and ALDH−CD44− cells isolated from SKOV3 and OVCAR3 cells. f Relative cell viability of ALDH+CD44+ and ALDH−CD44− SKOV3 cells after treatment with or without 20 μM cisplatin for 48 h, determined with the XTT assay. g Relative lactate production of ALDH+CD44+ and ALDH−CD44− SKOV3 cells after 24 h incubation. h Extracellular acidification and i OCR assays of ALDH+CD44+ and ALDH−CD44− SKOV3 cells after 2 h incubation measured using the glycolysis and extracellular oxygen consumption assays, respectively (RFU: relative florescence units). Relative PDK4 j mRNA and k protein expression of ALDH+CD44+ and ALDH−CD44− SKOV3 cells via qPCR and immunoblotting, respectively. l (Left) Representative images of xenograft tumours resected from mice inoculated with ALDH+CD44+ and ALDH−CD44− SKOV3 cells (n = 4). Resected tumours were re-inoculated into the flanks of the second batch of mice. (Right) Summary of tumour incidence and estimated frequency of ALDH+CD44+ and ALDH−CD44− SKOV3 cells determined via in vivo limiting dilution and self-renewal assays (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, results are presented as means ± SD from three independent experiments).