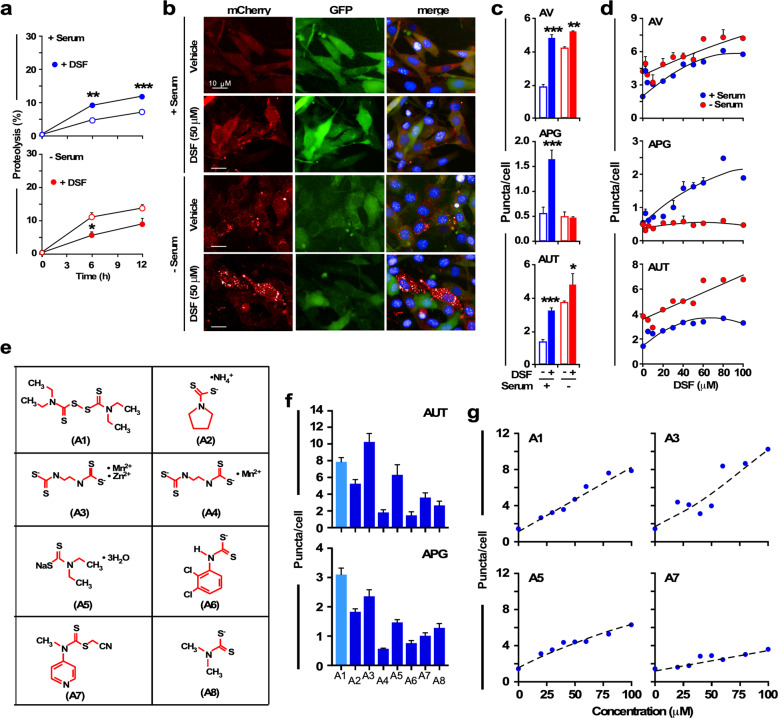
Fig. 4. Disulfiram activates autophagy in cultured cells.
a Effect of disulfiram (DSF) on the degradation of long-lived proteins. Murine NIH3T3 fibroblasts in culture were labeled with 3H-leucine for 48 h and incubated in complete (serum+) or serum-free medium in the presence of 20 μM DSF or not. Rate of proteolysis was calculated as the percentage of the initial acid-precipitable radioactivity (proteins) transformed into acid-soluble radioactivity (amino acids and small peptides) at the indicated times. All values are mean ± SEM of three independent experiments, each performed with triplicate wells per time point. There is no error bar in the top panel because the error bar is shorter than the size of the symbol. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 vs. without DSF. b–d Effect of DSF on basal and inducible autophagy. NIH3T3 cells expressing the tandem reporter mCherry-GFP-LC3 were exposed to 50 μM DSF for 24 h in complete (+Serum) or serum-free medium (−Serum). b Representative images of the individual and merged channels in cells where nuclei were highlighted by DAPI staining; c The number of autophagic vacuoles (AV), autophagosomes (APG), and autolysosomes (AUT) was determined by high-content microscopy. d Dose dependence of the activating effect of DSF on macroautophagy was analyzed in cells exposed to increasing concentrations of DSF. Number of AV (top panel), APG (middle panel), and AUT (bottom panel) was determined by high-content microscopy. e–g Structure activity of dithiocarbamate analogs on autophagy. e Structures of the eight compounds tested. f mCherry-GFP-LC3 reporter-expressing NIH3T3 cells were exposed for 24 h to 100 μM of DSF (A1) and DSF analogs (A2–A8) for the measure of AUT (top panel) or APG (bottom panel). g Changes in the number of AUT after exposure to increasing concentrations of A1, A3, A5, and A7. c–g Unless otherwise indicated, all values are mean ± SEM and quantifications were done in at least 2500 cells per condition in three different experiments using high-content microscopy. Abbreviations: A1, bis(diethylthiocarbamate) disulfide aka disulfiram; A2, ammonium pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate; A3, Mn2+-Zn2+ ethylenebis(dithiocarbamate); A4, Mn2+ ethylenebis(dithiocarbamate) aka pestanal; A5, Na+ diethyldithiocarbamate trihydrate; A6, triethylammonium N-(3,4-dichlorophenyl) dithiocarbamate; A7, S-cyanomethyl-N-methyl-N-(pyridin-4-yl) dithiocarbamate; A8, Zn2+ dimethyldithiocarbamate. Related to Supplementary Fig. 4.