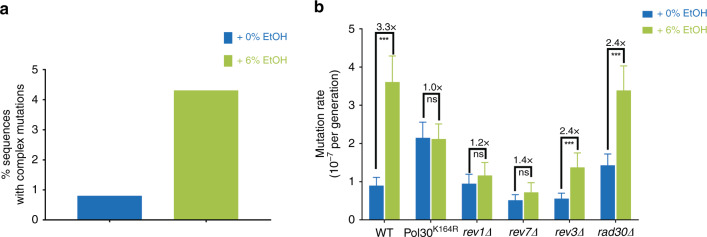
Fig. 7. Mutagenic effect of ethanol depends on error-prone polymerases.
a A trend for more complex mutations in ethanol-exposed cells. Complex mutations are defined as multiple mutations within ten nucleotides. For 0% EtOH, a total of 121 colonies were analyzed; for 6% EtOH, a total of 113 colonies were analyzed. b Ethanol-associated mutagenesis depends on error-prone polymerases and ubiquitination of Pol30 at Lys164. Cells (VK111, VK3831, VK3548, VK3614, MVP1101, and MVP1105) were grown in synthetic media (2% glucose), supplemented with the indicated ethanol concentrations (v/v). For each strain and condition, 54 cultures were analyzed. Data represent mutation rate estimates, as determined by fluctuation assays on canavanine. Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals. Statistical significance of differences in mutation rates was assessed using a likelihood ratio test. ***P < 0.001, ns nonsignificant. Specifically, p-values are 0 for WT, 9.99 × 10−1 for pol30 mutant, 0.25168 for rev1∆, 0.1036 for rev7∆, 1.8445 × 10−6 for rev3∆ and 1.1643 10−9 for rad30∆. Source data for this figure are provided as a Source Data file.