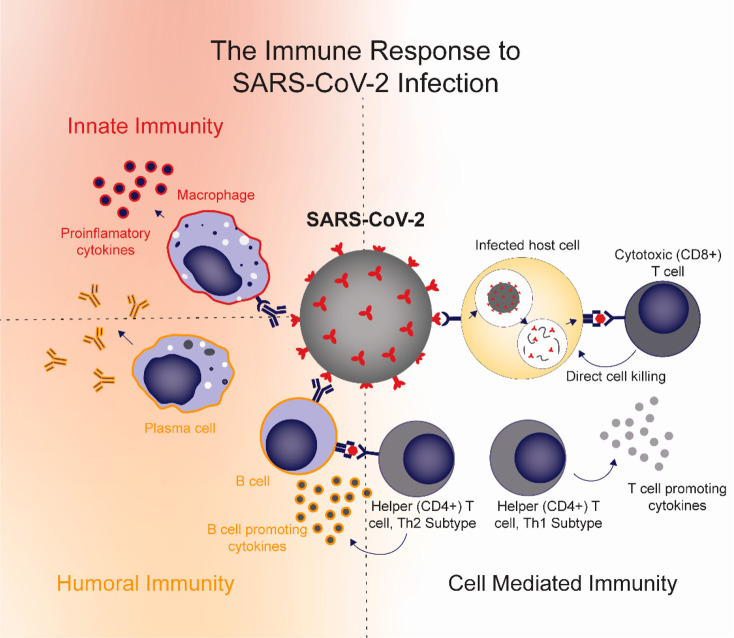
Figure 1.
Immune response to SARS-CoV-2 infection. Activation of inflammatory macrophages and subsequent production of proinflammatory cytokines is associated with adverse outcomes, including lung injury, during SARS-CoV-2 infection. Antibodies from humoral immunity can link adaptive immunity and innate immunity through Fc receptor interactions, leading to inflammatory activation of macrophages. Humoral immunity can also help promote viral clearance when targeted to appropriate parts of the virus. T cells have been shown to play an important role in viral clearance and recovery. CD8+ cytotoxic T cells, in particular, have been associated with favorable outcomes. Helper T cells can be of the Th1 subtype, which promote T cell activity, or the Th2 subtype, which link cell-mediated and humoral immunity by promoting B cell activity.