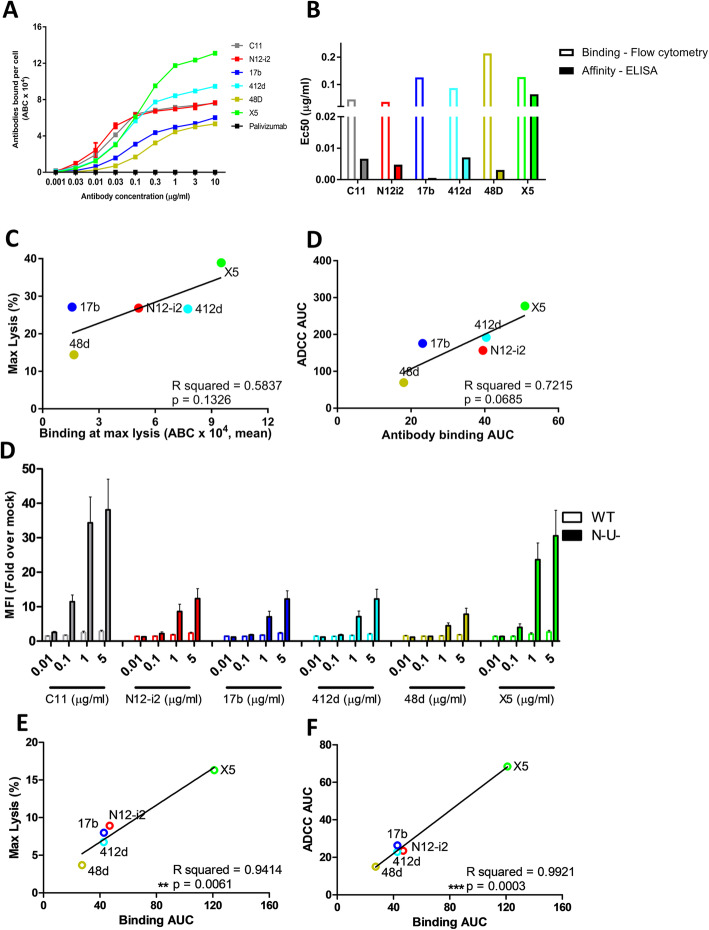
Fig. 6.
Correlations between antibody affinities, binding levels, and ADCC activity. a Number of antibodies bound per cell to GFP-CEM-NKR-CCR5-SNAP target cells coated with gp120 BaL. Quantum MESF beads were used to quantify the number of AF647-labeled antibodies bound per cell (ABC) to GFP-CEM-NKR-CCR5 target cells coated with gp120 BaL. n = 3, data is mean ± SEM. b EC50 of antibodies bound per cell to GFP-CEM-NKR-CCR5-SNAP target cells coated with gp120 BaL (hollow bars) and EC50 of antibody binding to full-length single chain (FLSC) (solid bars). c Correlations between the antibody binding levels to GFP-CEM-NKR-CCR5-SNAP target cells coated with gp120 BaL and ADCC parameters: maximum lysis vs. the number of antibodies bound at the concentration resulting in maximum lysis (left panel), area under the curve (AUC) of ADCC vs. antibodies bound (right panel) (d) Antibody binding to pNL4/ADA and pNL43/ADA/N-U- infected CEM-NKR target cells over a range of antibody concentrations. n = 3, data is mean ± SEM. e Correlations between the antibody binding levels to NL43/ADA/N-U- infected cells and ADCC parameters: ADCC maximum lysis vs. binding area under the curve (left panel), NL43/ADA/N-U- ADCC area under the curve vs. binding area under the curve (right panel). **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 via a two-tailed Pearson correlation. Individual data is supplied in Additional files 9 and 10