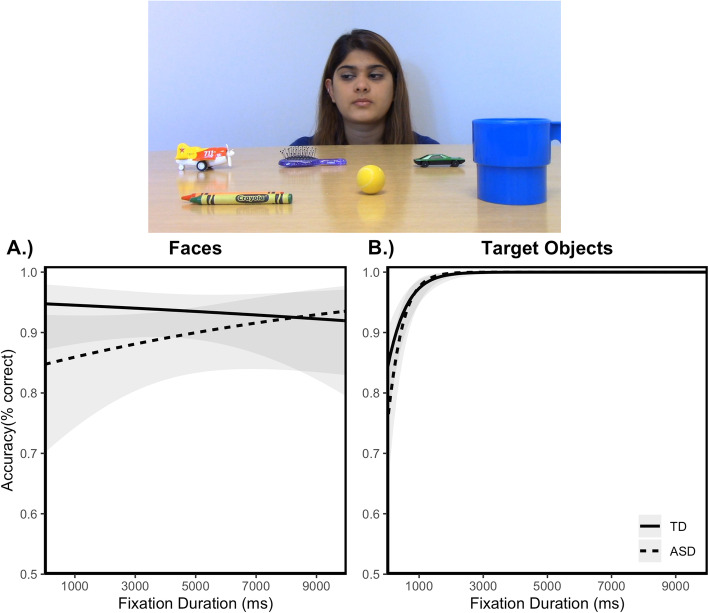
Fig. 2.
Association between visual attention and behavior during gaze following. Probability of identifying correct target object as a function of fixation duration to face, plotted as a function of group (a). There was no association between fixation duration to faces and performance in either group. Probability of identifying correct target object as a function of fixation duration to target object, plotted as a function of group (b). Longer fixation duration to target objects was associated with improved task performance for both groups. Shaded region reflects 95% confidence intervals. All plots reflect model-predicted relationships based on the mixed-effect models