FIGURE 7.
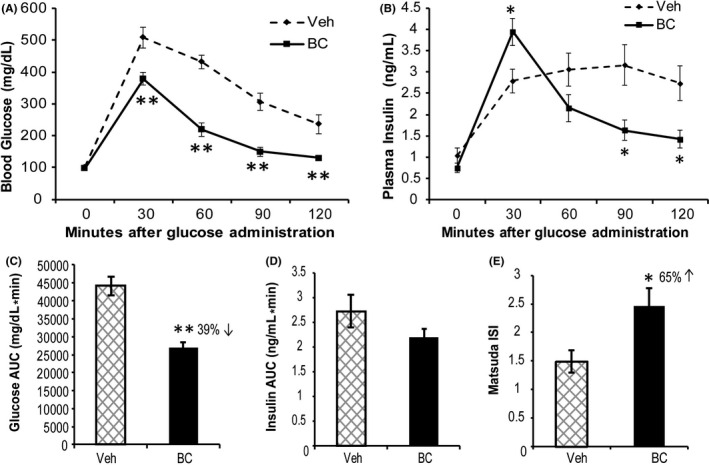
Bromocriptine treatment improves glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity in HFD‐fed rats. A GTT was performed after 14 days of treatment with bromocriptine (BC) (7.5 mg/kg, ip) or vehicle (Veh) daily at the onset of locomotor activity (ZT13.5). Compared with vehicle, such bromocriptine treatment reduced blood glucose levels during the GTT (A) with a 39% reduction in glucose area under curve (AUC) (P < .0001) (C). Bromocriptine increased the GTT plasma insulin peak at 30 min while reducing plasma insulin levels at 90 and 120 min during the GTT (B) with insulin AUC reduced 19% (ns) (D). Bromocriptine increased insulin sensitivity by 65% as revealed by Matsuda ISI (P = .015) (E). An asterisk denotes a significant difference verses control (*P < .05, **P < .01)
