Figure 3.
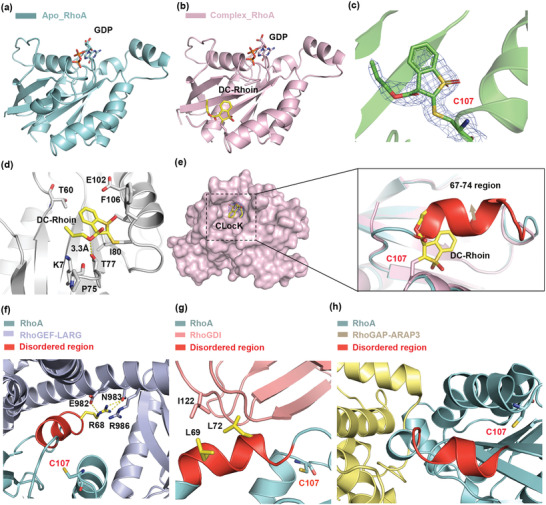
DC‐Rhoin covalently binds to RhoA and induces CLocK allosteric pocket. a) The crystal structure of apo‐RhoA (four‐cysteine mutant of RhoA, PDB code: 6KX2). b) The crystal structure of RhoA in complex with DC‐Rhoin (PDB code: 6KX3). c) The 2Fo‐Fc electron density map of compound DC‐Rhoin with the Cys107 residue, in the solved complex structure with RhoA. The contour level was set to 1.0 sigma. d) A close up view of the interaction between RhoA and DC‐Rhoin. The ligand and interacting residues are shown as sticks; hydrogen bonds are indicated by yellow dotted lines. e) Compared to the crystal structure of RhoA apo form, the helix with residues number 67‐74 (shown in red) was disordered in the crystal structures of RhoA with compound DC‐Rhoin. The novel pocket CLocK was stabilized and captured by compound DC‐Rhoin. f–h) The interaction surface of RhoA with RhoGEF‐LARG (PDB code: 1X86), RhoGDI (PDB code: 1CC0) and RhoGAP‐ARAP3 (PDB code: 5JCP).
