Figure 3.
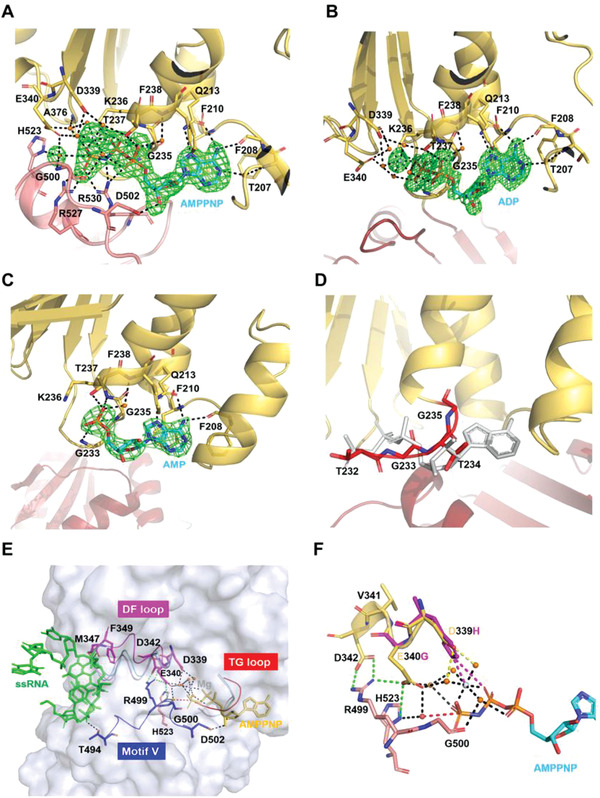
The ATPase sites of DDX21. A) Representation of the ATPase sites in DDX21‐RNA‐AMPPNP complex, with the electron density map (F o – F c) for AMPPNP‐Mg2+ and the presumptive catalytic water rendered at 3.0 σ. The broken red line connects the probable attacking water and the γ‐phosphorus atom. Arg204 is omitted for clarity. B) The ADP binding sites in DDX21‐ADP complex, with the electron density map (F o – F c) for ADP‐Mg2+ rendered at 3.0 σ. Arg204 is omitted for clarity. C) The AMP binding sites in DDX21‐AMP complex, with the electron density map (F o – F c) for AMP rendered at 3.0 σ. D) The potential ATP binding sites in the DDX21‐apo structure. The “TG loop” is colored in red. The modeled AMPPNP is colored in gray. E) Stereo view of the link between ATP binding pocket and RNA binding pocket, with the surface representation of DDX21‐ssRNA‐AMPPNP (gray). In the DDX21‐ssRNA‐AMPPNP structure, the “DF loop” is indicated in magenta, motif V (and Va) in blue, the “TG loop” in red, AMPPNP in yellow and RNA in green. In the DDX21‐apo structure, the “DF loop” is colored in light blue, and the “TG loop” is colored in red. Both of the “DF loop” and “TG loop” were colored in cyan in the DDX21‐ADP structure and light pink in the DDX21‐AMP structure. Green broken lines show the inter‐domain interactions. F) Superimposition of D339H and E340G mutants. D339H forms a new salt bridge (purple) with ATP phosphate and new cooperative bond (purple) with Mg2+ ion by the His substitution, while E340G mutation lacks the inter‐domain interactions with Arg499 and His523. Yellow broken lines show the interaction of Asp339 with Mg2+, mediated by water. Green broken lines show the inter‐domain interactions of Glu340 with Arg499 and His523 and inter‐domain interaction of Asp342 with Arg499. The broken red line shows the interaction between the presumptive attacking water and the γ‐phosphorus atom.
