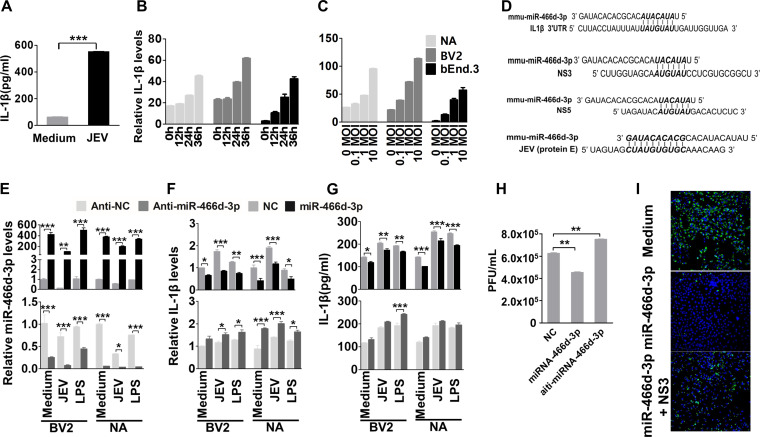
FIG 4.
miR-466d blockade enhances IL-1β secretion and promotes JEV replication (A) Homogenized mouse brains were collected at 9 dpi, and IL-1β expression in the mouse brains was determined by ELISA. (B and C) Cell supernatants from NA cells were collected at the indicated infection time points and infection doses, and IL-1β expression was determined by qRT-PCR and ELISA. (D) Introduction of miR-466d-3p binding sites in IL-1β, NS3, NS5, and E. miR-466d-3p sequences complementary to the coding sequences of IL-1β, NS3, NS5, and E are indicated in boldface italic. (E to G) The synthetic mimic of miR-466d-3p reduced IL-1β expression and blocked JEV replication, and the inhibitor of miR-466d-3p had the opposite effect. NA or BV2 cells were infected/treated with JEV at an MOI of 0.01, LPS (100 ng/ml), or medium control. After 48 h of infection/treatment, the cells were transfected with a mimic of miR-466d-3p or inhibitor of miR-466d-3p. (E) After 6 h of transfection, total RNA from NA cells was used to quantify the relative expression of miR-466d-3p (versus the negative control) by qRT-PCR. (F) After 6 h of transfection, total RNA from NA cells was used to quantify the relative expression of IL-1β (versus the negative control) by qRT-PCR. (G) After 6 h of transfection, cell supernatants were collected to quantify IL-1β expression by ELISA. (H) After 24 h of transfection, cell supernatants were collected to determine the JEV titer. (I) miR-466d target site-fused GFP was cotransfected with NS3 and/or miR-466d-3p mimic, and after 48 h of transfection, the cells were stained with DAPI (4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole). Fluorescence was observed under a fluorescence microscope. For all graphs, results are shown as means and SD. Significance was assessed using Student's t test. *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001.