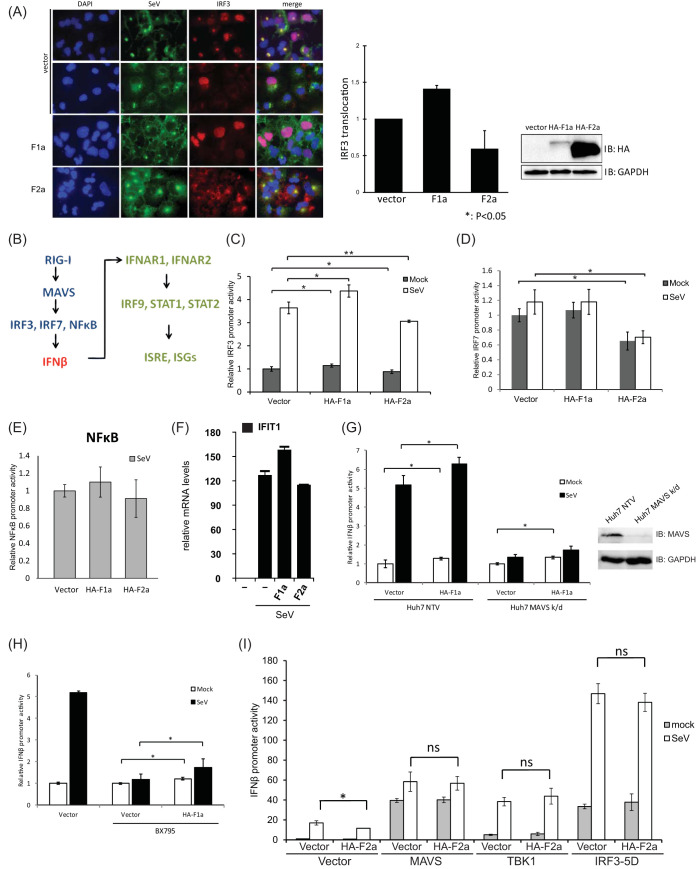
FIG 2.
F proteins affect downstream of MAVS and upstream of IRF3. (A) The genotypic effects of HCV F proteins in nuclear translocalization during SeV infection. Huh7 cells that were transfected with either HA-F1a or HA-F2a were split into 2 halves at 24 h posttransfection. One-half of the cells were lysed, and the expression levels of HA-F1a and HA-F2a were determined by anti-HA immunoblotting. Another half of transfected cells were then plated and infected with 100 HAU/ml of SeV for 18 h. The cells were fixed and stained with chicken anti-SeV and rabbit anti-IRF3 antibodies followed by fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-labeled anti-chicken (green) and Cy3-labeled anti-rabbit (red) antibodies. The nucleus was stained by 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (blue). (B) An illustration of simplified RIG-I mediated IFN-β induction and response pathways. (C) The genotypic regulation of IRF3 promoter activity by F proteins in Huh7 cells. Huh7 cells were cotransfected with pIRF3-Luc, pCMV-RLuc, and plasmids expressing F proteins. At 24 h posttransfection, cells were infected with SeV (100 HAU/ml) for 18 h and then lysed to detect luciferase and renilla luciferase activities. IRF3 promoter activity was increased in F1a protein-expressing cells and decreased in F2a protein-expressing cells. (D) IRF7 promoter activities in F protein-expressing Huh7 cells. Huh7 cells were cotransfected with pIRF7-luc, pCMV-RLuc, and plasmids expressing F proteins. At 24 h posttransfection, cells were infected with SeV (100 HAU/ml) for 18 h and then lysed to detect luciferase and renilla luciferase activities. The IRF7 promoter activity was decreased in genotype 2a F protein-expressing cells. (E) NF-κB promoter activities in F proteins expressing Huh7 cells. Huh7 cells were cotransfected with pNFκB-Luc, pCMV-RLuc, and plasmids expressing F proteins. At 24 h posttransfection, cells were infected with SeV (100 HAU/ml) for 18 h and then lysed to detect luciferase and renilla luciferase activities. The NF-κB promoter reporter was not affected by either F1a or F2a expression. (F) mRNA levels of IFIT1 during SeV infection in F1a- and/or F2a-expressing cells. The mRNA levels of IFIT1 correlate with the IFN-β promoter activities observed during SeV infection in F1a- and/or F2a-expressing cells. (G) IFN-β promoter activities in F1a-expressing Huh7 MAVS k/d cells. Immunoblotting of Huh7 NTV cells and Huh7 MAVS k/d cells confirmed the expression levels of MAVS in these cells. Huh7 MAVS k/d cells were cotransfected with pIFN-β-Luc, pCMV-RLuc, and plasmids expressing F proteins. At 24 h posttransfection, cells were infected with SeV (100 HAU/ml) for 18 h and then lysed to detect luciferase and renilla luciferase activities. Although MAVS was knocked down, the IFN-β promoter activity was still greater in F1a protein-expressing cells and reduced in F2a protein-expressing cells compared to the control vector-transfected cella. (H) F1a protein controls downstream of TBK1. Huh7 were cotransfected with pIFN-β-Luc, pCMV-RLuc, and plasmids expressing F1a. At 24 h posttransfection, the cells were then treated with BX795 (10 μM) for 6 h, followed by SeV (100 HAU/ml) infection for 18 h. The cells were then lysed to detect luciferase and renilla luciferase activities. Enhanced IFN-β promoter activity in genotype 1a-expressing cells was still observed before and after SeV infection. (I) HA-F2a and a series of constructs, including MAVS, TBK1, and IRF3-5D, were cotransfected into Huh7 cells with pIFN-β-Luc and pCMV-RLuc. At 24 h posttransfection, cells were infected with SeV (100 HAU/ml) for 18 h and then lysed to detect the IFN-β promoter activities in these cells by luciferase reporter assays. **, P < 0.01; *, P < 0.05.