Figure 5. The D664A Point Mutation Attenuated C99ΔC-Induced Dendritic Spine Loss in Postsynaptic CA1 Neurons.
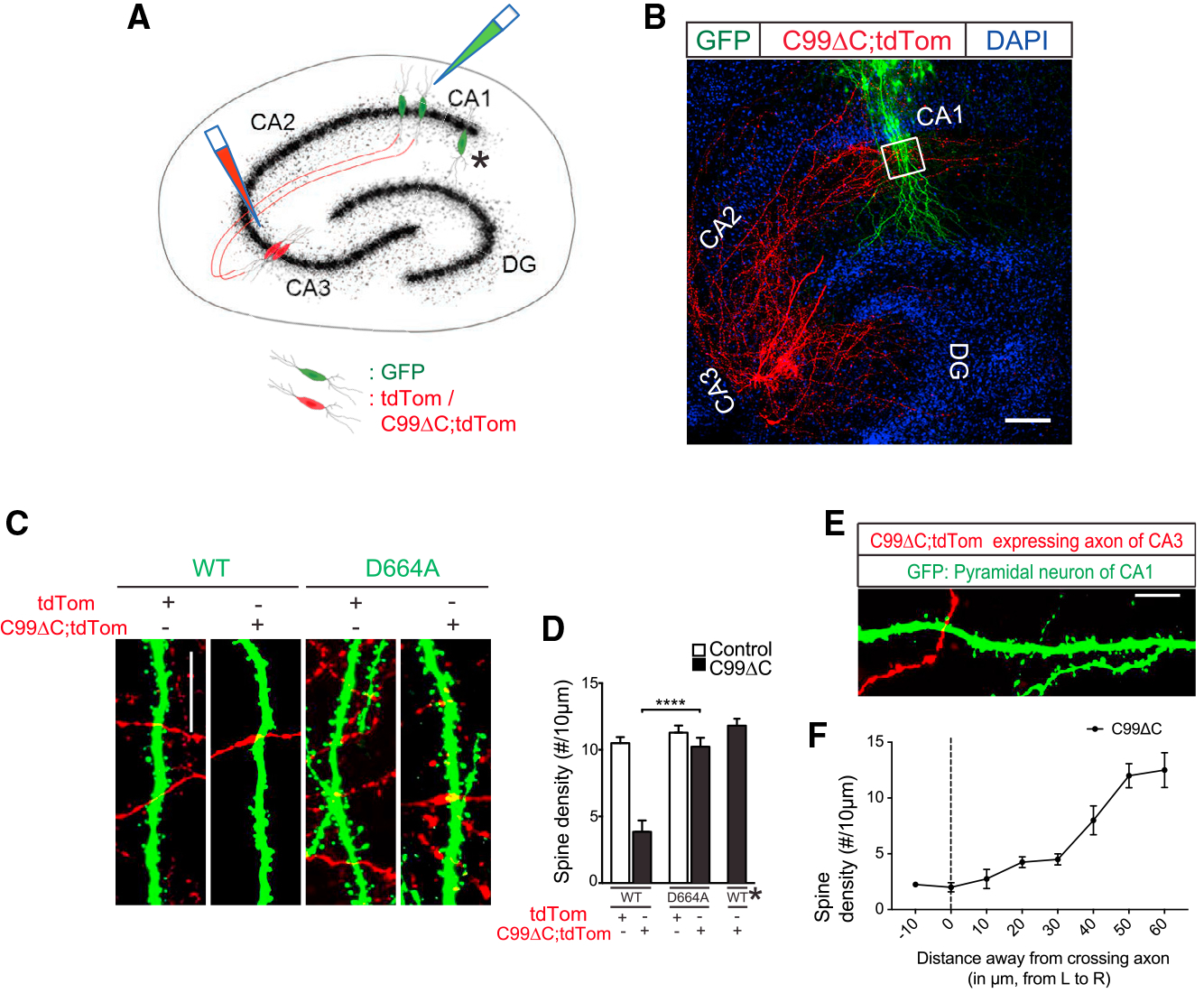
(A) Schematic of OTSCs infected with dual Sindbis viruses expressing C99ΔC and tdTomato or tdTomato alone in CA3 and GFP in CA1 neurons, respectively. Asterisk indicates region where CA1 pyramidal neurons were not innervated by tdTomato-labeled axonal projections from CA3 neurons. (B) Representative low-magnification image of OTSCs expressing two different fluorescent proteins in CA1 and CA3 neurons diagrammed in (A). Cell bodies and projects of axons and dendrites can be readily seen (red). The axons of CA3 pyramidal neurons labeled by tdTomato project to dendritic fields and cell bodies of GFP-labeled CA1 neurons (green) in this low-magnification image. DAPI was used to counterstain nuclei of hippocampal neurons. White box indicates region where spine densities were quantified. Scale bar, 100 μm. (C) Representative labeled dendritic segments of CA1 dendrites in OTSCs of WT and APP D664A KI mice showing tdTomato-labeled axons (red) from CA3 neurons within the same microscopic fields of GFP-labeled CA1 dendrites (green). Scale bar, 20 μm. (D) Quantification of dendritic spines from (C). The C99ΔC expression induced about 60% spine loss in CA1 dendrites but was absent in slices from APP D664A KI mice. CA1 dendrites not receiving afferent inputs from tdTomato-positive axons (asterisk here and in A) did not show spine loss. n = 12 neurons (tdTomato) and n = 14 neurons (C99ΔC) from 12 APP D664AKI mice; n = 9 neurons (tdTomato), n = 15 neurons (C99ΔC), and n = 11 neurons (non-innervated region designated by asterisk) from 13 WT littermate control mice. NS, not significant; ****p ≤ 0.0001 by two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. (E) Representative image of dendritic fields of CA1 pyramidal neuron expressing GFP but with few CA3 axons expressing tdTomato. Scale bar, 20 μm. (F) Distance-dependent spine density loss. Quantification of image shown in (E) showed that proximity of dendrites closer to crossing axons (μm from left [L] to right [R]) infected with C99ΔC was negatively correlated with spine density (n = 15 neurons from 13 WT mice).
