Fig 4. Longitudinal course in an individual with HZ and secondary CSF escape.
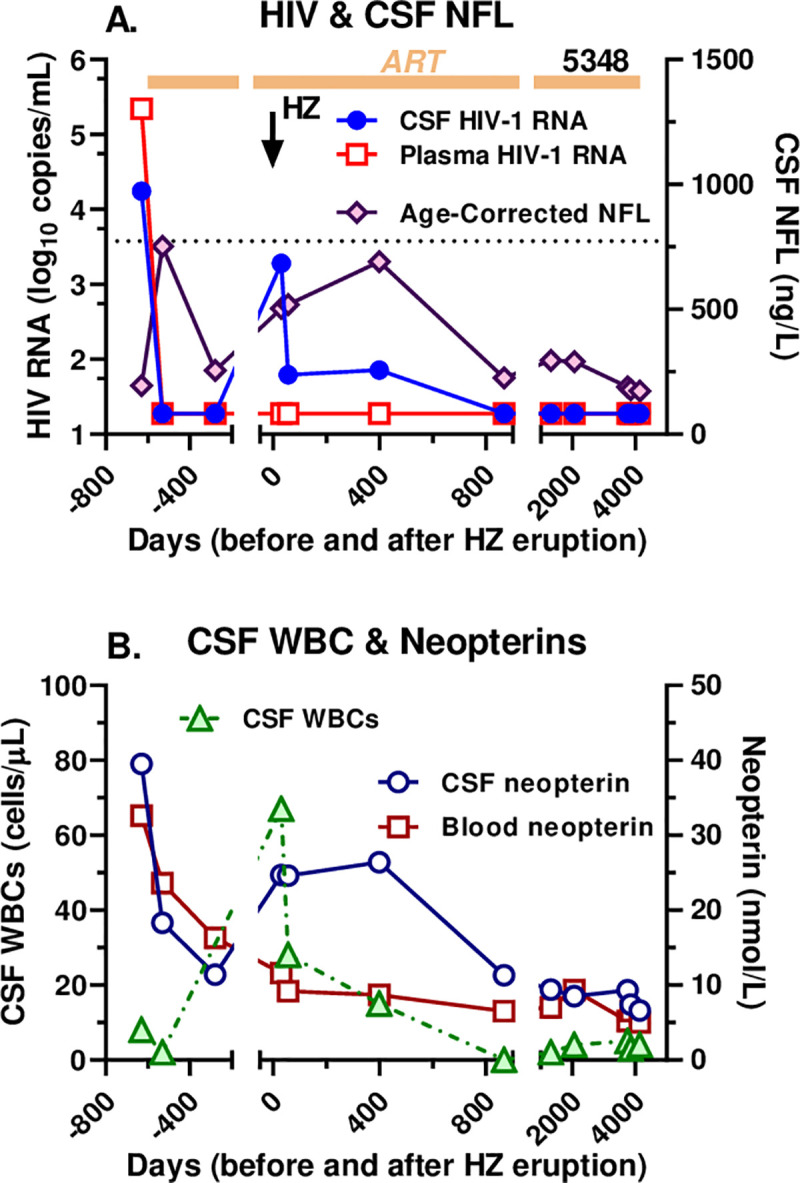
The two panels plot the long-term longitudinal course in HZ CSF escape subject 5348 from before initial treatment, through the HZ episode, to more than a decade later. A. shows the course of CSF and plasma HIV-1 RNA concentrations and age-corrected NfL. Most notable is the rise in CSF HIV-1 RNA after the HZ (time 0 designated by the downward vertical arrow) and its continued elevation for more than one year despite continued plasma HIV-1 suppression; CSF NfL also rose above baseline levels during this period. B. CSF WBC and CSF and blood neopterin over this same time course. The CSF WBC count rose after the HZ and remained abnormal for over a year, similar to the CSF HIV-1 RNA in panel A. The CSF neopterin also increased during the HZ episode and remained relatively high over the ensuing year before falling later while the plasma neopterin did not alter its trajectory with the HZ episode.
