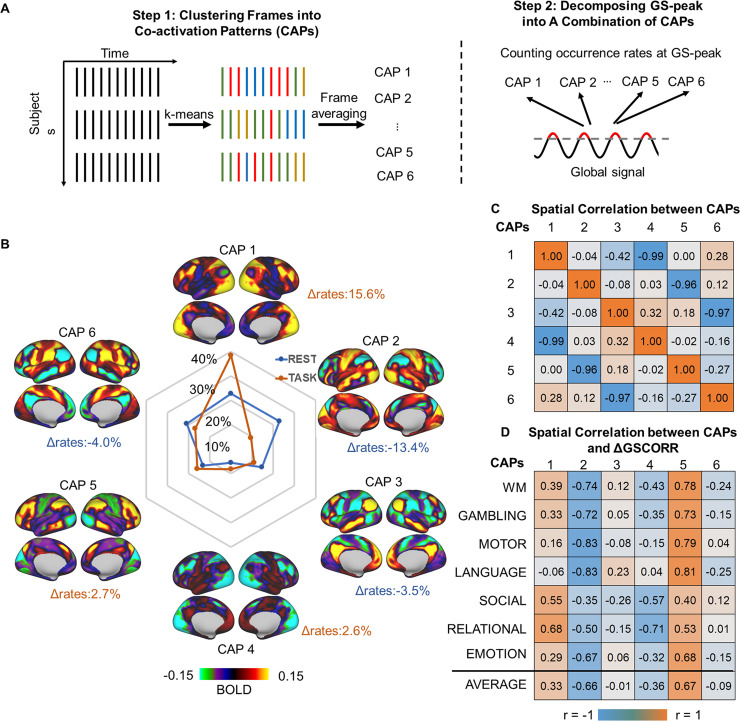
Fig 4. Transient CAPs at GS-peak.
(A) An illustration of the k-means clustering algorithm that partitions the whole-brain frames into spatially congruent CAPs (step 1), calculating the occurrence rate of each CAP at GS-peak (step 2). (B) Spatial topography of CAPs and their occurrence rates at the time points of GS-peak. Task modulation denoted the difference in the occurrence rate of the CAPs between task and rest (Δrate). (C) Spatial correlation between the CAPs. The six CAPs were composed of three pairs of opposite CAPS (i.e., CAP1 versus CAP4, CAP2 versus CAP5, and CAP3 versus CAP6), as shown by their spatially negative correlations. (D) Spatial correlation between the CAPs and the rest-task difference in GSCORR, i.e., ΔGSCORR. Data are available at Dryad: https://doi.org/10.5061/dryad.xsj3tx9bw. BOLD, blood oxygen level–dependent; CAP, coactivation pattern; GS, global signal; GSCORR, GS correlation; WM, working memory.