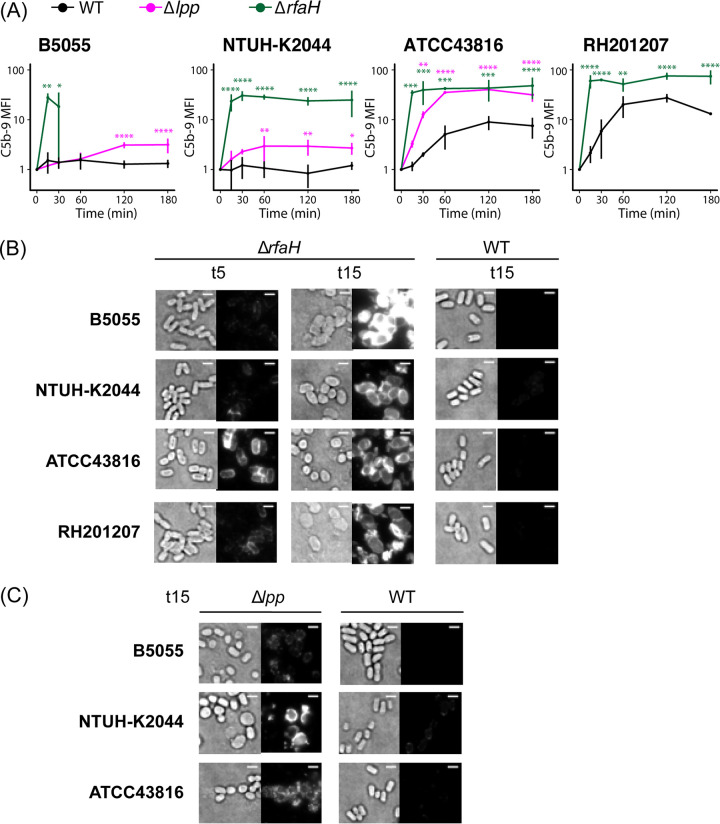
FIG 7.
C5b-9 binding to the bacterial cell surface. (A) Flow cytometry-based determination of C5b-9 formation on ATCC 43816, B5055, NTUH-K2044, RH201207, and their respective mutants after 15, 30, 60, 120, and 180 min of incubation in human pooled serum at 37°C (n = 3). Values were converted to AU, setting T0 to 1. Two-way repeated-measures ANOVA with uncorrected Fisher’s LSD test revealed significance as follows: *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001; ****, P ≤ 0.0001. For the B5055 ΔrfaH mutant, data were collected only at the first two time points due to cell lysis detected by release of cytoplasmic fluorescent marker from labeled cells. (B and C) Fluorescence microscopy of 5-min and 15-min serum-exposed ΔrfaH and WT cells (B) or 15-min serum-exposed Δlpp and WT cells (C) following incubation with mouse anti-C5b-9 antibody and AF488 goat anti-mouse IgG. Data are representative of three independent experiments. For comparison of binding patterns and intensity, transillumination (left) and fluorescence images (right) are normalized within each panel. Bar, 2 μm.