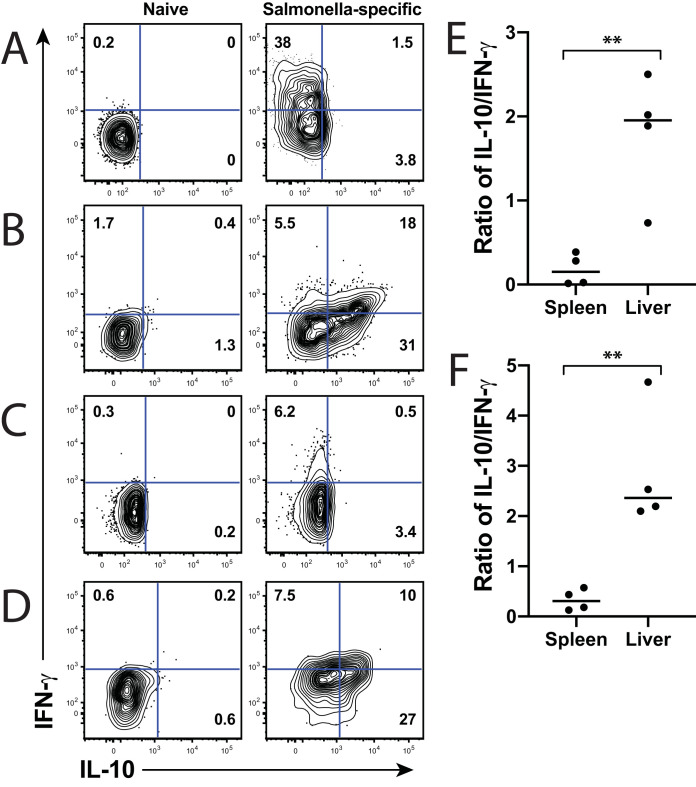
FIG 3.
Salmonella-specific lymphoid T cells produce predominantly IFN-γ, while liver T cells produce both IFN-γ and IL-10. (A and C) Spleens and (B and D) livers were harvested from (A and B) acutely or (C and D) chronically infected mice and stimulated with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA)/ionomycin for 2 h, then for an additional 4 h in the presence of brefeldin A. Cells were permeabilized, and intracellular cytokine staining was performed to measure IFN-γ and IL-10 production. Cytokine gates were set on naive (CD44low) CD4+ T cells, as shown in the left column for panels A to D. Representative flow plots are shown for each time point and tissue. Numbers in gates indicate percentage of cells positive for each cytokine. For (E) acute and (F) chronic times, the ratio of IL-10 to IFN-γ was calculated. A ratio of <1 indicates greater IFN-γ, while a ratio of >1 indicates greater IL-10. Unpaired Student’s t test was used to determine statistical significance between groups; **, P < 0.01. Combined from 2 experiments out of a total of 4 independent experiments.