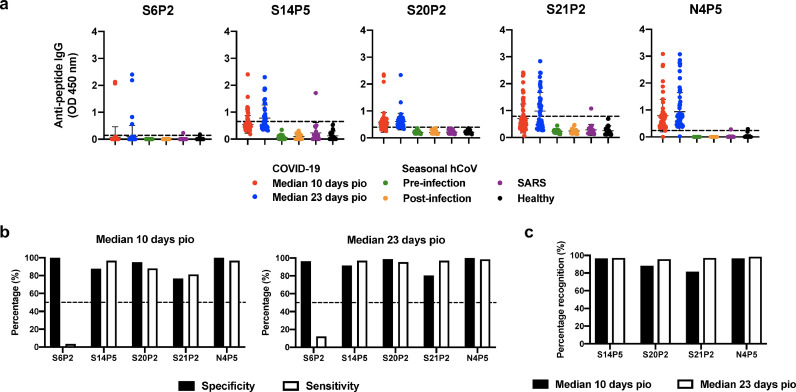
Fig. 2.
Specificity and sensitivity of putative IgG epitopes to detect anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies from COVID-19 patients. (a) Plasma samples from COVID-19 patients collected at timepoints of median 10 days post-illness onset (pio, n = 59) and median 23 days pio (n = 66), sera from seasonal hCoV-infected patients (n = 13) either pre- or post-infection, and plasma samples from recovered SARS patients (n = 20) and healthy donors (n = 22) were screened at 1:1000 dilution against five IgG-specific putative epitopes: S6P2, S14P5, S20P2, S21P2, and N4P5. Data are shown as mean ± SD of two independent experiments, with dotted lines indicating mean + 3SD of healthy donors. (b) Percentage specificity and sensitivity of putative epitopes to detect SARS-CoV-2-specific antibodies in plasma samples from COVID-19 patients during the timepoints of median 10 days pio (left panel) and median 23 days pio (right panel). Specificity and sensitivity values were derived from a threshold determined by the maximisation of the Youden's J statistic with a constraint that the threshold value has to be positive. (c) Percentage recognition of epitopes during the timepoints of median 10 days pio (black bars) and median 23 days pio (white bars).