Fig. 1. Overview of methods and data.
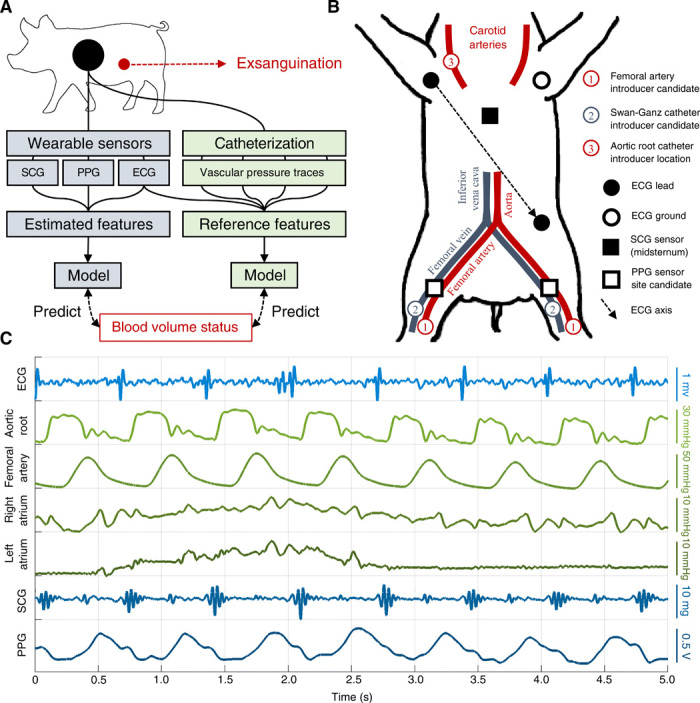
(A) Overall method used in this work. A wearable sensing system (blue) was used to develop a globalized model of BVS assessment, which was then compared with a catheter-based gold standard system (green). The catheter-based system directly measured aortic root, femoral artery, right atrial, and left atrial (via pulmonary capillary wedge) pressures. (B) Diagram of sensor placement during experiment. Each catheter was placed in one of the indicated candidate locations for each subject depending on artery and vein accessibility. The photoplethysmogram (PPG) sensor was then placed on the most accessible femoral artery branch. (C) Example traces obtained from wearable- (blue) and catheter-based (green) sensors during a single respiration cycle.
