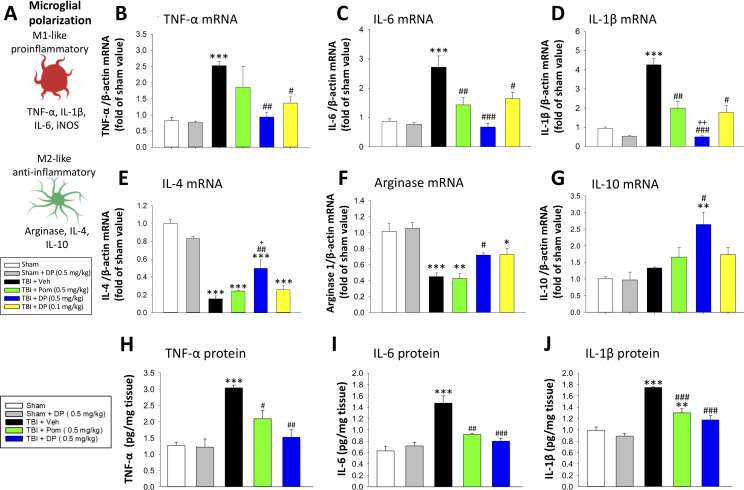
Figure 10. Post-injury treatment with DP or Pom significantly reduced TBI-induced cortical pro-inflammatory cytokine mRNA expression and protein levels.
(A) The expression levels of markers of a pro- and anti-inflammatory microglial (M1-, M2-like) state were quantified. TBI-induced significant elevations in mRNA levels of (B) TNF-α, (C) IL-6 and (D) IL-1β and declines in (E) IL-4 and (F) arginase-1 within the cortical contusion region, when evaluated 24 hr post injury. These changes were substantially and significantly mitigated by DP (0.1 and 0.5 mg/kg) and, to a lesser degree, by Pom (0.5 mg/kg) treatment, with DP 0.5 mg/kg demonstrating greater efficacy. (G) IL-10 mRNA levels were mildly elevated by TBI, and significantly elevated in the DP (0.5 mg/kg)-treated group. TBI-induced changes in pro-inflammatory cytokine mRNA expression were mirrored in protein levels (H, I, J), and DP (0.5 mg/kg) and, to a lesser extent, Pom (0.5 mg/kg) mitigated these. Mean ± S.E.M. (n = 5 in each group). ***p<0.001 vs. the Sham group. #p<0.05, ##p<0.01, ###p<0.001 vs. the TBI + Veh group. ++ p<0.01 vs. the TBI + Pom group.