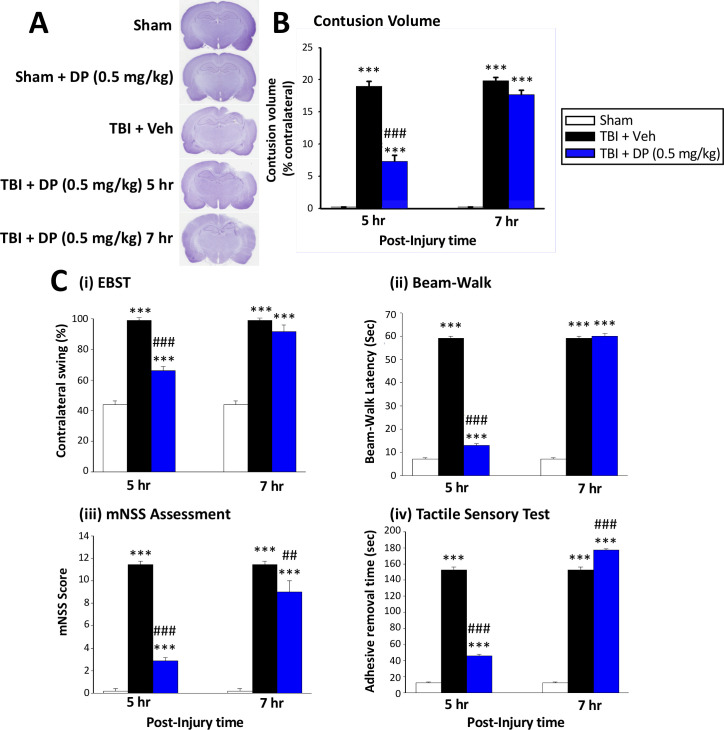
Figure 2. Intravenous administration of DP (0.5 mg/kg) at 5 hr but not at 7 hr after TBI significantly reduced contusion volume and behavioral impairments measured at 24 hr after TBI.
(A) Representative cresyl violet stained coronal brain sections from Sham (control without TBI), DP-treated Sham (Sham + DP 0.5 mg/kg), TBI-vehicle (TBI + Veh), and DP-treated TBI rats (TBI + DP, 0.5 mg/kg) following 5 or 7 hr treatment, (B) Intravenous administration of DP (0.5 mg/kg) at 5 hr but not at 7 hr after TBI induced a significant reduction in contusion volume relative to the TBI + Veh group. (C) Four separate behavioral outcome measures were quantified to evaluate TBI-induced deficits and their remediation by DP. These involved (i) postural asymmetry, as assessed by the elevated body swing test (EBST), (ii) motor coordination and balance measured by beam walking test, (iii) functional deficits appraised by the mNSS test, and (iv) sensory and motor function, revealed by latency in the adhesive removal test. Across all behavioral outcome measures, DP (0.5 mg/kg) significantly mitigated deficits when administered at 5 hr after TBI. Data represent the mean ± S.E.M. (n = 5 in each group). ***p<0.001 vs. Sham group; ##p<0.01, ###p<0.001 vs. TBI + Veh group.