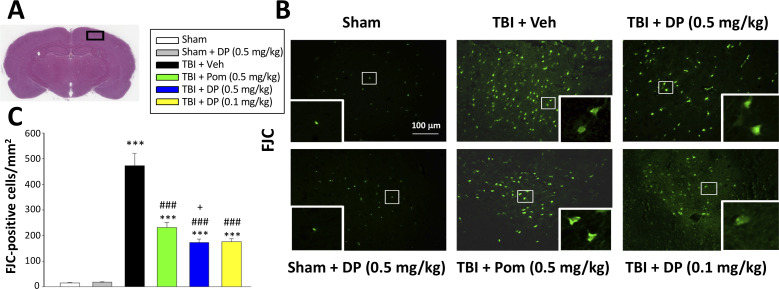
Figure 5. FJC staining confirms TBI-induced neurodegeneration within the contusion region, as well as significant mitigation by DP and Pom.
(A) Low power HE-stained coronal brain section from a sham animal showing area of evaluation (black rectangular box). (B) Representative photomicrographs showing the FJC-stained cortical region across animal groups at 24 hr after TBI. (C) Quantitative comparisons of mean densities of FJC-positive cells per field in the cortical contusion area at 24 hr post-injury. Notably, DP (0.1 and 0.5 mg/kg) and Pom (0.5 mg/kg) significantly reduced FJC positive neurons within the contusion area, with DP (0.5 mg/kg) showing significantly greater activity than the similar dose of Pom. Mean ± S.E.M. (n = 5 in each group). ***p<0.001 vs. the Sham group. ### p<0.001 vs. the TBI + Veh group. + p<0.05 vs. the TBI + Pom group. Scale bar = 100 μm.