Fig. 4.
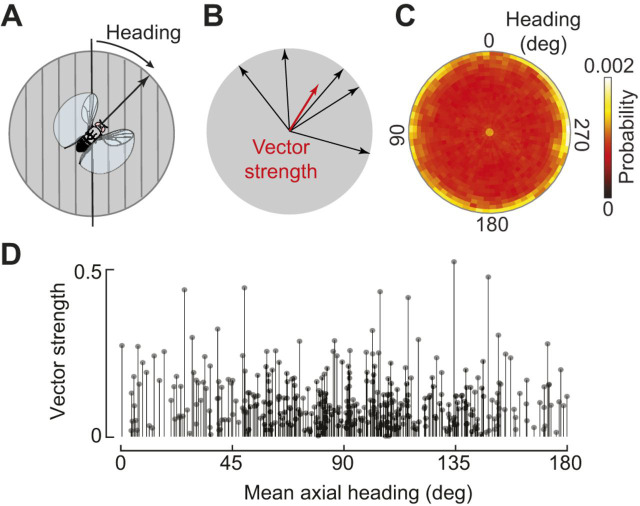
Drosophila perform menotaxis relative to a polarized light cue. (A) A fly's heading is defined as the angle between its longitudinal body axis and the polarization axis. At headings of 0 deg/180 deg, these two axes are aligned. (B) To calculate vector strength, a measure of heading consistency, flight headings are converted to unit vectors and summed. Vector strength ranges from 0 to 1, with 1 corresponding to a fly that precisely maintained the same heading. (C) A polar histogram showing the relative proportion of data at distinct combinations of heading and vector strength (denoted by angular and radial location in plot). Vector strength is computed over a 30 s time window to capture short-term stimulus stabilization. At the highest local vector strengths, flight data were distributed broadly across headings (N=372 flies; 93 h of flight data). (D) Mean axial heading for each flight (N=372) plotted against overall vector strength. Although the overall distribution was broad, there was a slight bias towards headings in which the polarization axis was perpendicular to the longitudinal body axis. Adapted from Warren et al. (2018).