Figure 4: Effect of nNOS on calcium handling.
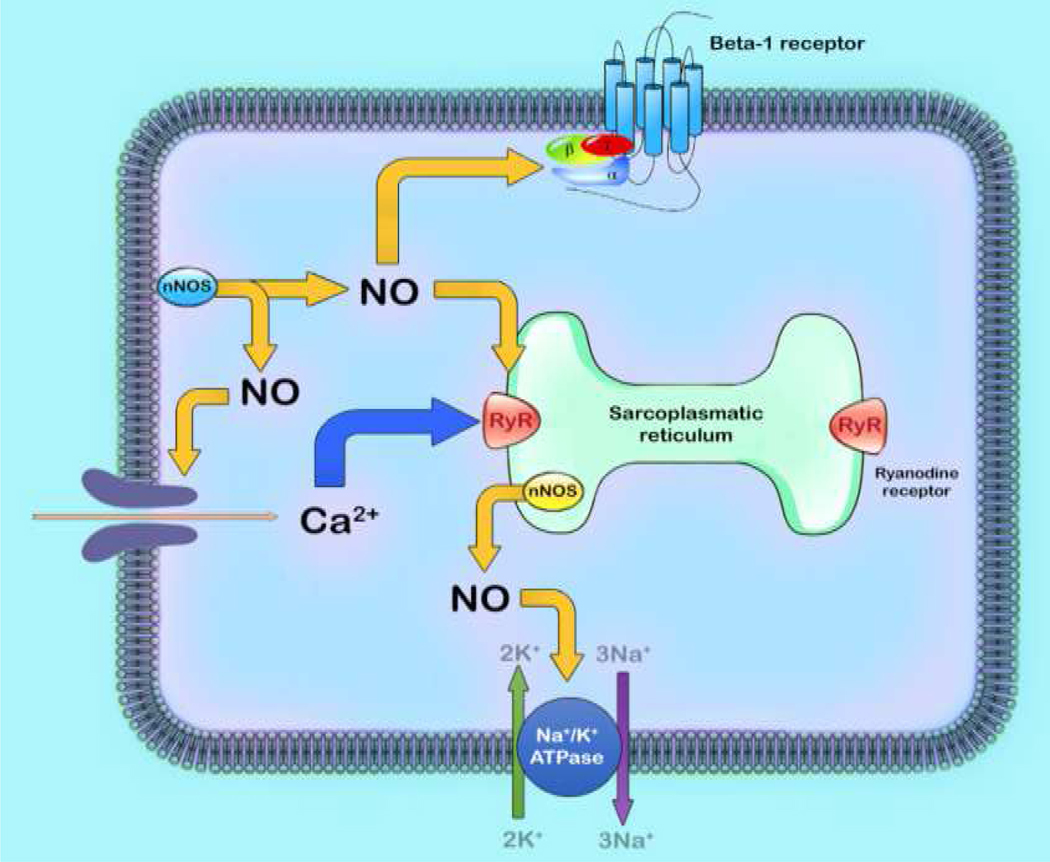
The process of excitation-contraction coupling begins with the entry of calcium (Ca2+) into the cell via the calcium current that triggers the further release of Ca2+ from sarcoplasmic reticulum. This stimulation of intracellular Ca2+ initiates and propagates contraction. Neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) have significant effects on myocyte contraction under basal conditions and via Beta-1 adrenergic receptor stimulation.
