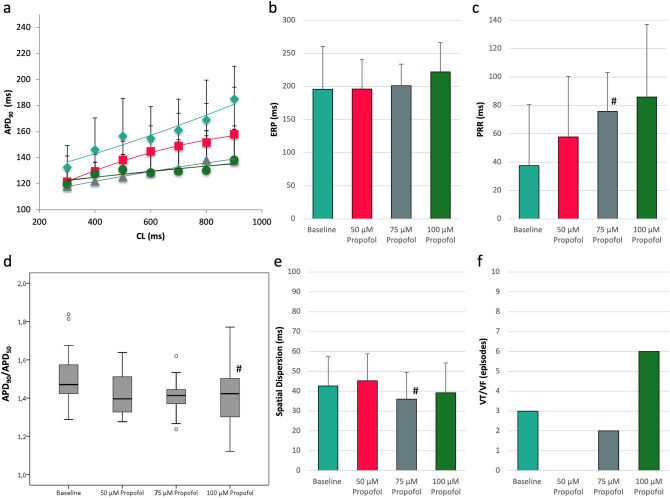
Figure 2.
(a) Cycle-length dependent APD90 under baseline conditions (filled rhombus) and after treatment with 50 µM (filled square), 75 µM (filled traingle) or 100 µM (filled circle) propofol. (b) Impact of propofol on effective refractory periods (ERP). (c) Concentration-dependent effect of propofol on post-repolarization refractoriness (#p < 0.05 compared to baseline conditions). (d) Box plots of the ratio of action potential duration at 90% of repolarization (APD90) and action potential duration at 50% of repolarization (APD50). A decrease in APD90/APD50 represents a rectangulation of action potential. (e) Influence of propofol treatment on repolarization heterogeneity as indicated by spatial dispersion of repolarization (#p < 0.05 compared to baseline conditions). (f) Occurrence of ventricular fibrillation (VF) tachycardia (VT) induced by programmed ventricular fibrillation.