Fig. 3.
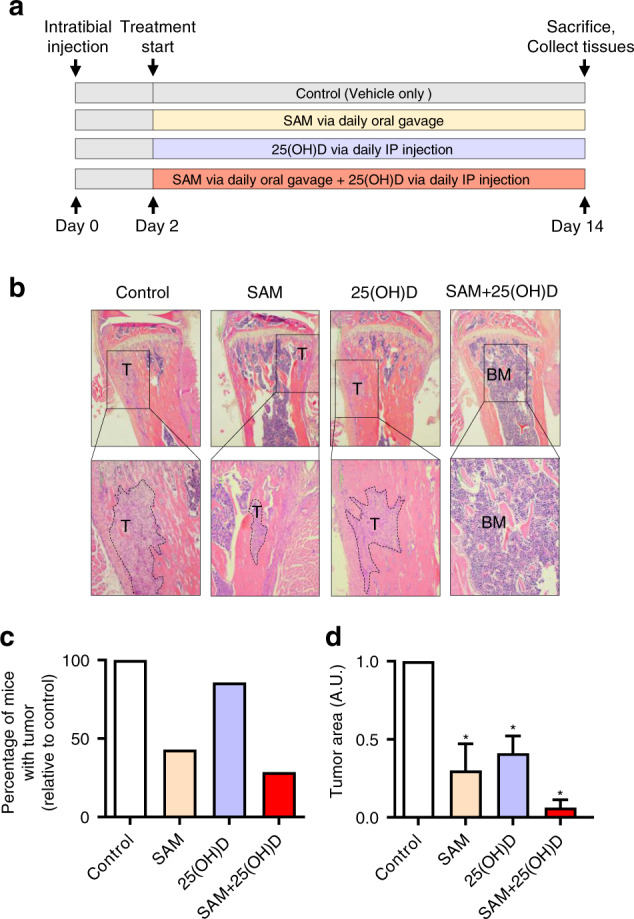
Effect of SAM, 25(OH)D, and their combination on breast cancer cell colonization to the bone in an intratibial model. a Schematic representation of treatment protocol used for treating female mice (FVB background) injected with PyMT-R221A cells and then treated with vehicle alone as control, SAM (160.0 mg·kg−1 per day) by daily oral gavage, 25(OH)D (40.0 ng·kg−1 per day) by intraperitoneal (i.p) injection, and SAM + 25(OH)D in combination from day 2 until day 14 when the mice were sacrificed (n = 9 animals per group). The tibias were collected from all animals and fixed for further histologic studies. b Representative low (×40; upper panel) and high (×100; lower panel) magnificaion images of the formalin-fixed histologic sections of the decalcified tibias from control and treated animals stained with Haemotoxylin and Eosin (H&E), where the tumors are marked a ‘T’ and bone marrow as ‘BM’. c Bar graph representing the percentage of mice that developed skeletal tumors in each group relative to the control group. d The relative area of tumor growth was quantified using the Fiji plugin (ImageJ), and the results are shown as mean ± SEM (n = 9 per group). Significant differences were determined using ANOVA followed by post hoc Tukey’s test and are represented by asterisks
